Understanding Genetics: Mutations, Chromosomal Aberrations, and Genetic Engineering
Genetic mutations can be harmless, harmful, or beneficial, leading to variations within a species. Examples of gene mutations and chromosomal aberrations, like Trisomy 21, illustrate genetic abnormalities. The increase in Down Syndrome cases with maternal age highlights a maternal age effect. Geneti
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Numerical Chromosome Aberrations in Humans
Numerical chromosome aberrations involve the gain or loss of whole chromosomes, impacting the genome size and potentially leading to genetic mutations. Nondisjunction, where chromosomes fail to separate properly during cell division, can result in aneuploidy - the presence of an extra or missing chr
0 views • 18 slides
Exploring Biomedical Gene Dosage Compensation in Trisomy 21
This instructional material focuses on teaching gene dosage compensation in the context of addressing the inactivation of one copy of Chromosome 21 in trisomy 21. The activity is designed for courses in Molecular Gene Regulation and Genetics, aiming to enhance students' understanding through hands-o
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Down Syndrome: Causes, Effects, and Characteristics
Down syndrome, also known as Trisomy 21, is a genetic condition caused by the presence of an extra 21st chromosome. Discovered by Dr. John Langdon Down in 1866, this condition affects individuals in various ways, influencing their development and abilities. People with Down syndrome may learn skills
0 views • 10 slides
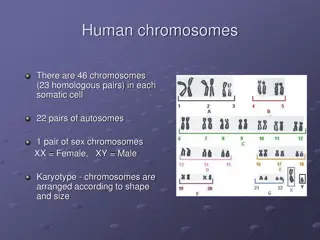
Understanding Chromosomal Disorders and Syndromes in Humans
Human chromosomes play a crucial role in determining genetic traits and health conditions. An extra copy of chromosome 21 leads to Down syndrome, while conditions like Klinefelter's syndrome, Turner's syndrome, Trisomy 13, 18, and 23 have distinct symptoms and implications. Trisomies result from abn
0 views • 20 slides
Understanding Down Syndrome: Types, Characteristics, and Impacts
Down syndrome is a genetic condition caused by an extra chromosome, typically chromosome 21. This leads to physical and cognitive challenges, with individuals exhibiting unique abilities. The syndrome presents with distinctive physical features, such as flattened face, almond-shaped eyes, and poor m
2 views • 14 slides