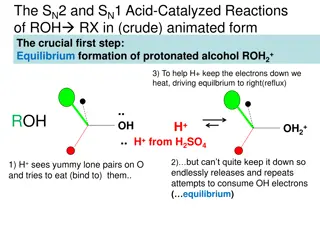
Acid-Catalyzed Reactions of Alcohols: SN2 and SN1 Mechanisms
The acid-catalyzed reactions of alcohols involve SN2 and SN1 mechanisms where protonated alcohols react with RX. In the SN2 mechanism, a nucleophile attacks a protonated 1o alcohol, leading to inversion. On the other hand, in the SN1 mechanism, a carbocation intermediate is formed, and a nucleophile
0 views • 12 slides
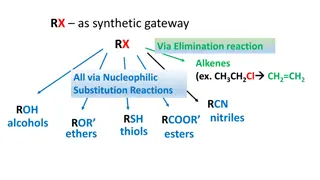
Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions: Factors Affecting SN2 Reactivity
Understanding the factors influencing SN2 reactions in synthetic gateways involving elimination reactions of alkenes is crucial for predicting reaction rates. This includes analyzing the impact of solvent types on reaction rates in different scenarios. Polar protic solvents and polar aprotic solvent
0 views • 19 slides
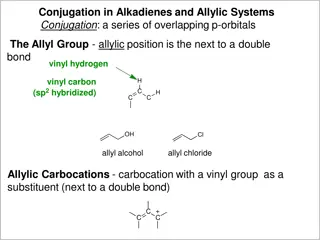
Understanding Allylic Systems and Reactions
Conjugation in alkadienes and allylic systems involves overlapping p-orbitals, with the allyl group featuring resonance-stabilized allylic carbocations. Allylic halides exhibit enhanced reactivity in SN1 and SN2 reactions, and allylic free radicals demonstrate distinct electron density patterns. Add
0 views • 25 slides