Comprehensive Overview of ABE Lab Manual and Foundations of Biotech Package
The ABE Lab Manual, authored by Doreen Osgood, MS, PhD, is a comprehensive resource for biotechnology education, including sequences like Genetic Engineering and Colony PCR. The manual includes teacher and student guides, along with related resources like PowerPoint presentations and lists of labora
1 views • 5 slides
REGULATION OF PLASMID COPY NUMBER
Plasmids regulate their copy number to maintain a balance that doesn't burden the host cell. Copy numbers vary based on factors like plasmid size and culture conditions. Plasmids are classified as stringent or relaxed based on replication control. Various systems, including counter-transcribed RNAs
4 views • 17 slides
Genetic Transformation: Introduction and Pre-Lab Inquiry
Explore the process of genetic transformation in the laboratory setting, focusing on inserting genes of interest into bacterial cells through recombinant DNA technology. Understand the role of restriction enzymes, plasmids, and genetic markers in this procedure. Engage in a pre-lab inquiry to identi
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Plasmid Partitioning Mechanisms in Bacteria
The stable maintenance of low-copy-number plasmids in bacteria relies on partition mechanisms that ensure proper positioning during cell division. Different from high-copy-number plasmids, which rely on random diffusion, low-copy-number plasmids require regulated partitioning mechanisms to prevent d
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding DNA Ligation Techniques for Molecular Biology Applications
DNA ligation involves joining DNA fragments to vectors to create new DNA or plasmids. Methods include DNA ligase, T4 ligase, and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase. Linkers and adaptors play a key role in DNA cloning experiments by generating sticky ends for DNA cloning. The use of adaptors allow
1 views • 13 slides
Understanding Recombinant DNA Technology and Cloning Vectors in Genetics Engineering
Exploring the fundamentals of recombinant DNA technology and gene cloning, this content delves into the key concepts and basic steps involved. It covers various cloning vectors such as plasmids, bacteriophages, and artificial chromosomes, highlighting their common features and applications in geneti
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding Plasmids: DNA Molecules Free of Chromosome
Plasmids are DNA molecules existing free of the chromosome in a cell. They can be circular or linear and carry genes beneficial to the host. Plasmids replicate from unique origins and regulate copy numbers through various mechanisms. Different replication mechanisms, such as theta and RC, are used,
0 views • 31 slides
Understanding Cloning Vectors and Recombinant DNA Technology
Genetics Engineering Lecture-2 delves into the concept and basic steps of recombinant DNA technology and gene cloning, highlighting different types of cloning vectors like plasmids, bacteriophages, bacterial artificial chromosomes, yeast artificial chromosomes, and mammalian artificial chromosomes.
1 views • 13 slides
Understanding DNA: A Journey from Friedrich Miescher to Genes and Function
DNA, the hereditary basis of life, was first discovered by Friedrich Miescher in 1869. It consists of chromosomes, plasmids, and organellar DNA, collectively known as the genome. Genes, sequences of DNA, encode proteins and RNA, essential for an organism's functions. The genome is divided into chrom
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Phage Vectors in Genetic Engineering
Phage vectors, utilized in genetic engineering, are bacteriophages capable of incorporating genes of interest into their genome. They have a higher DNA capacity compared to plasmids, making them ideal for creating genomic libraries. Bacteriophages like Lambda and M13 are commonly used for cloning ve
0 views • 17 slides
Mechanisms and Role of Horizontally Transferred Genetic Elements in Bacterial Disease Pathogenesis
This presentation explores the transfer of foreign DNA into bacteria, discussing mechanisms such as conjugation, transduction, and transformation. It delves into the significance of Mobile Genetic Elements (MGEs) like plasmids, bacteriophages, and transposons in bacterial virulence and pathogenesis.
0 views • 20 slides
Basic Biology of Plasmid and Phage Vectors
Plasmids are replicons inherited extrachromosomally, existing as circular DNA molecules. They can be categorized as conjugative or non-conjugative based on transfer genes presence, and by copy number per cell. Linear plasmids and their maintenance mechanisms are also discussed, along with phenotypic
0 views • 13 slides
Understanding Recombinant DNA Technology and Plasmid Vectors
Explore the world of recombinant DNA technology through the utilization of plasmids as vectors for gene cloning. Learn about techniques like insertional inactivation and the characteristics of common plasmid vectors such as pBR322. Discover the intricacies of genetic manipulation in bacterial origin
0 views • 26 slides
Understanding DNA Structure and Genetic Information Encoding
Complementary nitrogenous bases in DNA, pyrimidines (thymine, cytosine) and purines (adenine, guanine), store biological information through antiparallel strands. DNA, with non-coding regions, undergoes replication and transcription to RNA for protein synthesis. Nucleic acids, DNA, and RNA are cruci
0 views • 7 slides
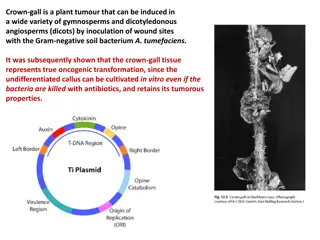
Understanding Crown Gall Disease in Plants
Crown gall is a plant tumor induced by the soil bacterium A. tumefaciens, resulting in oncogenic transformation. Opine metabolism plays a central role in the disease, with Ti-plasmids carrying T-DNA responsible for unregulated growth and opine synthesis. Border sequences on the Ti-plasmid are crucia
0 views • 17 slides
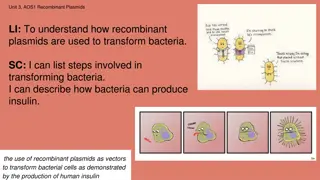
Understanding Recombinant Plasmids in Bacterial Transformation
Recombinant plasmids play a crucial role in transforming bacteria for producing proteins like insulin. The process involves steps such as uptake through methods like heat shock or electroporation, culturing with antibiotics, and selection of transformed cells. By introducing human genes into bacteri
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding CIDAR MoClo Labs in Synthetic Biology Teaching
In CIDAR MoClo Labs, students learn DNA engineering concepts, construction of plasmids, and analysis of fluorescent data. Background knowledge of DNA, proteins, bacterial plasmids, and the LacZ method is required. Skills include pipetting, DNA measurement, bacterial transformation, and plate reader
0 views • 19 slides