Understanding Logical Form and Equivalence in Conditional Statements
Delve into the intricacies of logical form, equivalence, and compound statements in the realm of propositional logic. Explore valid and invalid arguments, conditional statements, and the logic of compound statements with puzzles to sharpen your logical reasoning skills. Unravel scenarios like determ
2 views • 81 slides
Understanding Inference and Vyapti in Logic
Inference, known as Anumana in Sanskrit, is the process of deriving knowledge based on existing information or observations. It can be used for personal understanding or to demonstrate truths to others. An inference may be SvArtha (for oneself) or ParArtha (for others). Vyapti, the invariable concom
1 views • 14 slides
Understanding Inference in Indian Philosophy
In Indian philosophy, inference is considered one of the six ways to attain true knowledge. It involves three constituents: Hetu (middle term), Sadhya (major term), and Paksha (minor term). The steps of inference include apprehension of the middle term, recollection of the relation between middle an
11 views • 8 slides
Understanding Resolution in Logical Inference
Resolution is a crucial inference procedure in first-order logic, allowing for sound and complete reasoning in handling propositional logic, common normal forms for knowledge bases, resolution in first-order logic, proof trees, and refutation. Key concepts include deriving resolvents, detecting cont
2 views • 12 slides
Understanding the Scope of Inference in Statistical Studies
Statistical studies require careful consideration of the scope of inference to draw valid conclusions. Researchers need to determine if the study design allows generalization to the population or establishes cause and effect relationships. For example, a study on the effects of cartoons on children'
1 views • 15 slides
Logical Expressions and Symbolism in Sentential Logic
Understanding sentential logic, logical expressions, and symbols through examples of logical reasoning and inference. Explore the concepts of logical OR, AND, negation, and the complexities of inclusive and exclusive logic in various scenarios.
1 views • 33 slides
DNN Inference Optimization Challenge Overview
The DNN Inference Optimization Challenge, organized by Liya Yuan from ZTE, focuses on optimizing deep neural network (DNN) models for efficient inference on-device, at the edge, and in the cloud. The challenge addresses the need for high accuracy while minimizing data center consumption and inferenc
0 views • 13 slides
Understanding Boolean Algebra and Logical Statements
Introduction to Boolean algebra, logical statements, and compound statements. Explore the concepts of Boolean variables, logical operators, writing conventions, equivalence in Boolean algebra, and truth tables. Learn how to analyze and evaluate logical expressions using truth tables.
1 views • 25 slides
Understanding the Difference Between Observation and Inference
Learn to differentiate between observation (direct facts or occurrences) and inference (interpretations based on existing knowledge or experience) through examples such as the Sun producing heat and light (observation) and a dry, itchy skin leading to the inference that it is dry. The distinction be
2 views • 14 slides
Understanding Boolean Algebra and Logical Statements
Boolean Algebra allows for formalizing logical reasoning using variables that can be either true or false. It involves logical statements, compound expressions, logical operators like AND, OR, NOT, writing conventions, equivalence, and truth tables to determine the truth values of statements. By und
0 views • 25 slides
Reading Comprehension Inference Activities
Engage in reading comprehension with these inference activities. Analyze passages, make logical deductions, and answer questions to enhance critical thinking skills. Explore scenarios, draw conclusions, and strengthen your reading comprehension abilities through these interactive exercises.
2 views • 21 slides
Navigating Statistical Inference Challenges in Small Samples
In small samples, understanding the sampling distribution of estimators is crucial for valid inference, even when assumptions are violated. This involves careful consideration of normality assumptions, handling non-linear hypotheses, and computing standard errors for various statistics. As demonstra
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Propositional Logic and Logical Operators
Learn about propositional logic, statements, logic operators, compound statements, exclusive-or, logical equivalence, and writing logical formulas for truth tables. Explore how to create compound statements for exclusive-or using different approaches and ensure logical equivalence. Enhance your know
0 views • 26 slides
Understanding Rules of Inference in Logic
Dive into the world of logic with this detailed exploration of rules of inference. Learn about different types of arguments, such as Modus Ponens and Modus Tollens, and understand how to determine the validity of an argument. Discover the purpose of rules of inference and unravel the logic behind co
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Logical Relations in Programming Languages
Explore the concept of logical relations in programming languages, focusing on the relation between high-level and low-level programs. Learn about contextual equivalence, its benefits and limitations, and how logical relations offer a robust framework for defining program equivalence. Discover why l
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Logical Inference: Resolution in First-Order Logic
Resolution in logic is a crucial inference procedure that is both sound and complete for unrestricted First-Order Logic. It involves deriving resolvent sentences from clauses in conjunctive normal form by applying unification and substitution. This approach covers various cases such as Modus Ponens,
3 views • 12 slides
Rules of Inference in Discrete Math Exercises
In this exercise, two arguments are presented involving logical reasoning in Discrete Mathematics. The solutions explain the application of rules of inference for each step in the arguments. The exercise explores implications and deductions based on given premises to draw valid conclusions.
0 views • 5 slides
Analyzing Validity of Arguments in Discrete Math
This exercise assesses the validity of arguments in discrete mathematics by identifying logical errors or applying rules of inference. The solutions provided highlight fallacies such as affirming the conclusion, modus tollens, and denying the hypothesis. Understanding these principles is crucial for
0 views • 4 slides
Understanding Laws of Logic and Logical Reasoning
Laws of logic play a crucial role in reasoning and making deductions. This comprehensive guide explains the use of contrapositives, examples of conditional statements, and the significance of laws like the Law of Syllogism. Understanding these principles helps in effectively analyzing statements and
0 views • 8 slides
Rules of Inference Exercises and Solutions in Discrete Mathematics
Explore exercises and solutions in discrete mathematics focusing on rules of inference. Analyze logical premises and draw relevant conclusions using rules such as modus tollens, modus ponens, and disjunctive syllogism. Understand the application of these rules in different scenarios to reach valid d
0 views • 4 slides
Understanding Expert Systems and Knowledge Inference
Expert Systems (ES) act as synthetic experts in specialized domains, emulating human expertise for decision-making. They can aid users in safety, training, or decision support roles. Inference rules and knowledge rules play key roles in ES, helping in problem-solving by storing facts and guiding act
0 views • 63 slides
Understanding Knowledge-Based Agents: Inference, Soundness, and Completeness
Inference, soundness, and completeness are crucial concepts in knowledge-based agents. First-order logic allows for expressive statements and has sound and complete inference procedures. Soundness ensures derived sentences are true, while completeness guarantees all entailed sentences are derived. A
0 views • 6 slides
Fast High-Dimensional Filtering and Inference in Fully-Connected CRF
This work discusses fast high-dimensional filtering techniques in Fully-Connected Conditional Random Fields (CRF) through methods like Gaussian filtering, bilateral filtering, and the use of permutohedral lattice. It explores efficient inference in CRFs with Gaussian edge potentials and accelerated
0 views • 25 slides
Probabilistic Graphical Models Part 2: Inference and Learning
This segment delves into various types of inferences in probabilistic graphical models, including marginal inference, posterior inference, and maximum a posteriori inference. It also covers methods like variable elimination, belief propagation, and junction tree for exact inference, along with appro
0 views • 33 slides
Understanding Symbolic Logic and Rules of Inference
Explore the realm of symbolic logic and rules of inference through Modus Ponens, Well Formed Formulas (WFFs), truth tables, and more. Discover how logic is topic-neutral and test arguments for validity using truth tables. Dive into the world of logical equivalence and consistency with practical exam
0 views • 15 slides
Optimizing Inference Time by Utilizing External Memory on STM32Cube for AI Applications
The user is exploring ways to reduce inference time by storing initial weight and bias tables in external Q-SPI flash memory and transferring them to SDRAM for AI applications on STM32Cube. They have questions regarding the performance differences between internal flash memory and external memory, r
0 views • 4 slides
Typed Assembly Language and Type Inference in Program Compilation
The provided content discusses the significance of typed assembly languages, certifying compilers, and the role of type inference in program compilation. It emphasizes the importance of preserving type information for memory safety and vulnerability prevention. The effectiveness of type inference me
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Meaning, Relations, and Rules of Inference in Logic
Exploring the concept of meaning, relations, and rules of inference in logic through the use of truth tables to evaluate logical formulas. Discover how tautologies and contradictions are identified, and how logical operators influence the truth values of propositions. Delve into examples that showca
0 views • 24 slides
Identify the Error in Logical Inference: Discrete Math Exercise 14
The exercise presents an argument based on logic where it is incorrectly concluded that Lola is happy based on the given premise. The solution points out that while there exists an x that satisfies the premise, it does not necessarily mean Lola is one such x. This highlights the importance of carefu
0 views • 4 slides
Understanding Distributed System Synchronization and Logical Clocks
Continuing from the previous lecture on time synchronization, this session delved into logical clock synchronization, mutual exclusion, and election algorithms in distributed systems. Logical clocks, such as Lamport's Clock and Vector Clock, play a crucial role in defining the order of events withou
0 views • 33 slides
Understanding Compound Statements in Logic
The summary discusses the logic of compound statements, covering logical form, equivalence, tautologies, contradictions, conditional statements, valid and invalid arguments, and more. It explains the definitions of statements, negation, conjunction, disjunction, statement form, logical equivalence,
0 views • 12 slides
Rules of Inference Exercise Solutions in Discrete Math
This content provides solutions to exercises involving rules of inference in discrete mathematics. The solutions explain how conclusions are drawn from given premises using specific inference rules. Examples include identifying whether someone is clever or lucky based on given statements and determi
0 views • 4 slides
Modern Likelihood-Frequentist Inference: A Brief Overview
The presentation by Donald A. Pierce and Ruggero Bellio delves into Modern Likelihood-Frequentist Inference, discussing its significance as an advancement in statistical theory and methods. They highlight the shift towards likelihood and sufficiency, complementing Neyman-Pearson theory. The talk cov
0 views • 22 slides
Understanding Logical Agents and Propositional Logic in AI
Designing logical agents involves forming representations of the world, using inference for deriving new insights, and deducing actions based on these representations. Knowledge Base (KB) is a crucial component, comprising known facts and current percepts to infer hidden states. Propositional logic,
0 views • 23 slides
Sequential Approximate Inference with Limited Resolution Measurements
Delve into the world of sequential approximate inference through sequential measurements of likelihoods, accounting for Hick's Law. Explore optimal inference strategies implemented by Bayes rule and tackle the challenges of limited resolution measurements. Discover the central question of refining a
0 views • 29 slides
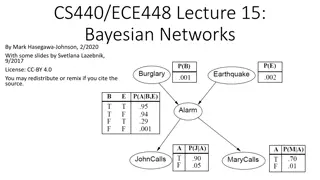
Understanding Bayesian Networks for Efficient Probabilistic Inference
Bayesian networks, also known as graphical models, provide a compact and efficient way to represent complex joint probability distributions involving hidden variables. By depicting conditional independence relationships between random variables in a graph, Bayesian networks facilitate Bayesian infer
0 views • 33 slides
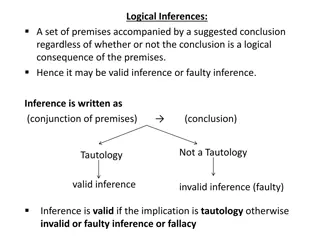
Understanding Logical Inferences and Rules of Inference
Logical inferences involve drawing conclusions from premises, which can either be valid or invalid based on the rules of inference. This includes Modus Ponens, Hypothetical Syllogism, DeMorgan's Law, and Law of Contrapositive. Invalid inferences result in fallacies like denying the antecedent. Exerc
0 views • 18 slides
Predicate Logic and Proofs in CSE 311
Explore the translation of statements into predicate logic, learn about inference proofs and nested quantifiers, and delve into the application of logical thinking in real-world scenarios. Discover a new way of constructing proofs and understand notation laws of inference. Engage in interactive proo
0 views • 37 slides
Advancements in Logical Natural Language Generation from Open-Domain Tables
Cutting-edge research in logical natural language generation (NLG) is transforming the field by moving beyond traditional surface realization to generate summarized text, conclude trends, and apply logical and mathematical operations. By addressing limitations such as lack of logical inference, summ
0 views • 33 slides
Dynamic Crowd Simulation Using Deep Reinforcement Learning and Bayesian Inference
This paper introduces a novel method for simulating crowd movements by combining deep reinforcement learning (DRL) with Bayesian inference. By leveraging neural networks to capture complex crowd behaviors, the proposed approach incorporates rewards for natural movements and a position-based dynamics
0 views • 15 slides