Applications of Radioisotopes in Nuclear Medicine
Nuclear medicine utilizes radioisotopes to provide crucial diagnostic information about the functioning of specific organs and to treat various conditions. Diagnostic techniques in nuclear medicine involve using radioactive tracers that emit gamma rays from within the body. Positron Emission Tomogra
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Geochemistry and Its Impact on Human Health
This session, led by Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi from the Department of Earth Science at UG, delves into the significance of geological elements in human health, discussing diseases arising from their deficiency or excess intake. Topics include geophagy, fluorine's impact on dental health, iodine defi
0 views • 48 slides
The Halogens: Properties and Uses of Fluorine, Chlorine, Bromine, Iodine, and Astatine
The halogens are a group of non-metals in the periodic table with seven electrons in their outer shell, making them highly reactive. This article discusses the properties and uses of fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine. Fluorine is utilized in toothpaste, chlorine is commonly used as a
0 views • 13 slides
Characteristics and Effects of Fluorine Release from Shallow High-Fluoride Soils
Shallow groundwater contaminated with high levels of fluorine poses a significant risk of fluorosis in areas like Gaomi, China. This presentation by Kyle Ziemba highlights the repercussions of fluorine release from soil into aquifers, leading to dental and skeletal damage. Experiments conducted in G
0 views • 12 slides
Group 17 Elements: The Halogens and Their Properties
Group 17 elements, known as the Halogens, include fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and astatine (At). They exhibit unique properties such as small atomic radii, high ionization energy, and strong oxidizing power. The halogens form diatomic molecules and have varying electron co
0 views • 19 slides
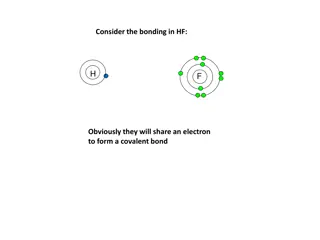
Understanding Bonding in HF Molecule
In HF bonding, hydrogen and fluorine share an electron to form a covalent bond. Fluorine, being more electronegative, attracts the bonding electrons more, resulting in a polar covalent bond. If hydrogen was less electronegative, the bonding electrons would shift further towards fluorine until an ion
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Electronic Configurations Through Simplified Assignments
Exploring electron configurations and orbital regions using simplified notations colored in on Periodic Charts. Descriptions and visual aids for Carbon, Fluorine, and excited state of Fluorine. Learn to assign s, p, d, and f electron neighborhoods without memorization through a fun song. Includes te
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Radioactive Decay and Half-Life in Nuclear Chemistry
Exploring the concept of radioactive decay and half-life in nuclear chemistry, this content covers the types of nuclear radiation, alpha decay of Uranium, and the significance of half-life in determining the decay of radioactive substances such as Carbon-14. An example with Fluorine-18 illustrates t
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding Group 17 Elements in Chemistry
Explore the properties, electron configurations, appearances, and industrial uses of Group 17 elements in the periodic table. Learn about nonmetals, metals, metalloids, and noble gases like fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine. Discover the industrial production and reactions of hydroge
0 views • 20 slides