Urban Development Models: Burgess and Hoyt
The Burgess concentric ring model and Hoyt sector model are key frameworks explaining urban social structures. Burgess's model illustrates urban land use in rings around the CBD, while Hoyt's model emphasizes outward growth along transportation arteries. Criticisms include applicability limitations
5 views • 13 slides
Understanding Sequential Logic Circuits in Digital Systems
Logic circuits in digital systems can be either combinational or sequential. Sequential circuits utilize storage elements along with logic gates, where outputs depend not only on present inputs but also on past inputs and internal states. They are essential building blocks, with storage registers pl
5 views • 20 slides
Earth-GRAM Overview and Update Status
Earth-GRAM is undergoing significant upgrades including updates to the Global Reference Atmospheric Model suite. The upgrade team aims to modernize code, incorporate state-of-the-art data sources, enhance user support, and address limitations. The team comprises experts from NASA Langley Research Ce
0 views • 22 slides
Overview of EV Infrastructure Load Model (EVIL) by Alexander Lonsdale
The EVIL model, developed by ADM, provides hourly electricity load shapes for transportation in commercial and residential sectors. It uses R executable scripts and static outputs to drive model output, facilitating scenario building for utility rate structures and energy forecasts. The model functi
2 views • 23 slides
A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions
Unified methodology for interpreting model predictions through additive explanations and Shapley values. It discusses the relationship between Additive Explanations and LIME, introduces Shapley values, approximations, experiments, and extensions in model interpretation. The approach unifies various
1 views • 21 slides
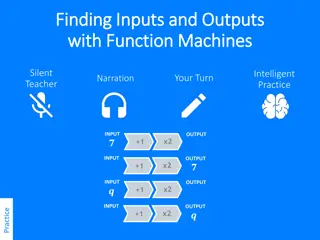
Understanding Function Machines: Finding Inputs and Outputs
Explore the concept of function machines, where inputs are transformed into corresponding outputs using a specific rule (in this case, x2 + 1). Engage in interactive exercises to practice finding missing inputs or outputs and solving for unknown values within the function machines.
0 views • 7 slides
Understanding Logic Circuits in Aircraft Systems
Aircraft logic systems follow MIL/ANSI standard logic symbols and conventions used in electronic applications. Inverters, buffers, AND gates, OR gates, NAND gates, NOR gates, Exclusive-OR gates, and Exclusive-NOR gates are commonly used in aircraft logic circuits. These gates have specific behaviors
0 views • 52 slides
Understanding the Logical Framework in Project Design
Project design involves creating a logical framework that outlines the project's key elements, including goals, purposes, outputs, and inputs. The matrix helps in displaying development hypotheses and monitoring and evaluation information, guiding the transformation of inputs into outputs to achieve
2 views • 11 slides
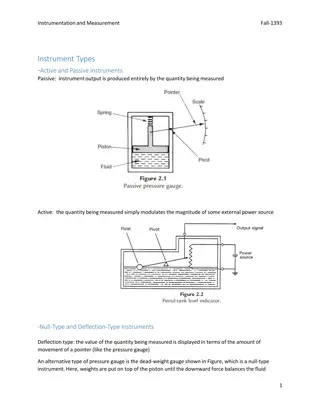
Understanding Instruments in Instrumentation and Measurement
Passive and active instruments play key roles in measurement, with null-type and deflection-type instruments providing different ways to display values. Analogue and digital instruments offer varying outputs, while indicating instruments and those with signal outputs serve different purposes. Smart
2 views • 12 slides
New Community Solar Financial Model for Fall 2021 Webinar Overview
Explore the latest updates and features of the new community solar financial model for Fall 2021 presented in the SAM webinars. Learn about the system owner's perspective, community solar financing mechanisms, and how subscribers can benefit from reductions in their electricity bills. Discover how t
2 views • 13 slides
Theoretical Derivation and Application of Nuclear Shell Model in Quantum Physics
Brought to you by Dr. Md. Rabiul Islam, Associate Professor at RGU, this presentation delves into the theoretical derivation of the shell model using Schrodinger wave equations in the presence of specific potentials. Exploring the solutions for the wave equation and explaining the role of quantum nu
1 views • 14 slides
Developing an Effective Logic Model: A Quick Guide
A logic model is a visual representation that illustrates the relationships between resources, activities, outputs, and outcomes of a program. By clarifying these elements, logic models enhance program effectiveness and aid in planning, implementation, and evaluation. They serve as a reference point
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding Electronic Systems and Programmable Components
Dive into the world of electronic systems and programmable components by exploring key terms, sensors like Light Dependent Resistor and Thermistor, control devices, circuit components, and flow charts. Learn about inputs, outputs, feedback loops, and how to design simple routines for controlling out
1 views • 6 slides
Understanding Production Systems and Processes
Production involves converting resources into goods or services efficiently to meet market demands. It encompasses manufacturing, mining, growing goods, and employing processes to transform inputs into outputs. A production system comprises inputs, conversion processes, and outputs to deliver finish
1 views • 21 slides
Project Contributions to GEF Focal Areas Outcomes and Outputs
Highlighting the project's contributions to various GEF focal areas outcomes and outputs, including biodiversity, climate change adaptation, mitigation, and more. The presentation covers strategic issues encountered, lessons learned from implementing a programmatic approach, and insights on upscalin
0 views • 7 slides
Understanding the OSI Model and Layered Tasks in Networking
The content highlights the OSI model and layered tasks in networking, explaining the functions of each layer in the OSI model such as Physical Layer, Data Link Layer, Network Layer, Transport Layer, Session Layer, Presentation Layer, and Application Layer. It also discusses the interaction between l
1 views • 41 slides
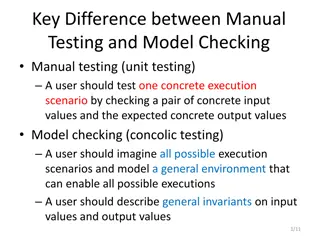
Difference Between Manual Testing and Model Checking
Manual testing focuses on testing specific scenarios with concrete inputs and outputs, while model checking involves imagining all possible scenarios to create a general environment for testing. In manual testing, users test specific execution scenarios, whereas in model checking, users envision and
2 views • 4 slides
Analyzing Agreement and Disagreement in High School RUAE Passages
This task involves identifying and explaining similarities or differences between arguments presented in two passages for the Higher RUAE (close reading) paper. The focus is on recognizing key areas of agreement or disagreement and providing supporting evidence from each passage to earn marks. Tips
1 views • 17 slides
MFMSA_BIH Model Build Process Overview
This detailed process outlines the steps involved in preparing, building, and debugging a back-end programming model known as MFMSA_BIH. It covers activities such as data preparation, model building, equation estimation, assumption making, model compilation, and front-end adjustment. The iterative p
0 views • 10 slides
Bonneville Power Administration Workshop: Preliminary Outputs and Updates
Bonneville Power Administration's workshop for BP-22 Rate Period showcased updates on load forecasts, system firm critical outputs, economic conditions, and energy models. Discussions included high-water mark processes, regional concerns, and future steps.
0 views • 33 slides
Introduction to Drude Model in Solid State Physics
Drude Model, formulated around 1900, explains the fundamental properties of metals such as electricity and heat. It proposes that electrons in metals behave like a classical electron gas, moving freely between atomic cores. The model considers the mean free path between electron collisions and estim
0 views • 39 slides
Enhancing Teaching Effectiveness through the Skill of Explaining
Skill of explaining plays a crucial role in the teaching-learning process by providing clear and concise explanations to students. It involves referencing previous knowledge, introducing new concepts, relating new knowledge to what students already know, using connecting links effectively, and avoid
0 views • 16 slides
MBA Program Assessment and Causal Model Analysis: Insights and Integration
Delve into the assessment value chain of the 2021-2022 MBA Report, exploring inputs, outcomes, impacts, and outputs to measure student learning outcomes and satisfaction. Analyze the causal model relationships affecting student satisfaction with learning, aiming to enhance outcomes and impacts for i
0 views • 13 slides
Understanding the PEEL Model for Effective Essay Writing
The PEEL model, which stands for Point, Example, Explanation, Linker, is a valuable tool for incorporating quotes in essays. It helps structure your arguments by focusing on the main point, supporting it with examples, explaining their relevance, and linking ideas logically. This model is illustrate
0 views • 8 slides
Challenges in Explaining the Data: A Research Agenda for the Future
Explore the complexities of explaining data, from understanding causality to interactive processes and visualizations. Judea Pearl's work on causality and Halpern's foundational research shape the emerging science of explaining data, highlighting the limitations and challenges faced by data analysts
0 views • 5 slides
High-Speed I/O Table-Driven Outputs Overview
Explore the capabilities of high-speed I/O table-driven outputs as showcased in the BX10, BX18, and BX36 devices. Learn about the discrete and analog input/output configurations, Ethernet ports, and high-speed features available in these devices. Additionally, understand how to set up and manage out
0 views • 13 slides
Understanding Finite State Machines in Digital Logic Design
Finite state machines play a crucial role in digital logic systems, allowing for the implementation of sequential circuit designs. These machines consist of states and transition functions, determining system behavior based on inputs and current state. The output function generates outputs based on
0 views • 35 slides
Evolution of Atomic Models: From Rutherford to Quantum Mechanics
Various atomic models have been proposed throughout history, starting with John Dalton's idea of atoms as tiny particles to J.J. Thomson's Plum Pudding model. Ernest Rutherford's discovery of the nucleus and Niels Bohr's quantum model of the atom revolutionized our understanding. Bohr's proposal of
0 views • 38 slides
CREST Demand Model v2.0 Eoghan McKenna & Murray Thomson
The CREST Demand Model v2.0, developed by Eoghan McKenna & Murray Thomson at Loughborough University, is a comprehensive simulation tool that analyzes the energy demand of dwellings. It considers factors such as solar thermal collectors, climate data, irradiance, electrical demand, temperature, gas
0 views • 4 slides
Positron Production Simulation Using Geant4: Detailed Overview
This comprehensive content discusses a positron production simulation program based on Geant4. It covers the simulation program description, primary generator input, outputs analysis, and areas for improvement including compatibility with G4-10.X and automation. The program involves generating gamma
1 views • 5 slides
Understanding Natural Language Generation (NLG) Process
Natural Language Generation (NLG) is the process of constructing natural language outputs from non-linguistic inputs. It involves generating text from machine representations to meet specific communicative goals. NLG is distinct from Natural Language Understanding (NLU) as it maps meaning to text, w
0 views • 38 slides
Principles of Econometrics: Multiple Regression Model Overview
Explore the key concepts of the Multiple Regression Model, including model specification, parameter estimation, hypothesis testing, and goodness-of-fit measurements. Assumptions and properties of the model are discussed, highlighting the relationship between variables and the econometric model. Vari
1 views • 31 slides
Understanding Gate Classifications in Digital Logic Design
Explore the world of gate classifications in digital logic design through topics such as primitive and complex gates, buffer gates, tri-state outputs, and more. Learn about the function and importance of different gate types like NAND, NOR, XOR, XNOR gates, and understand the necessity of using buff
0 views • 42 slides
Comprehensive Overview of OSCAR v3.1: A Compact Earth System Model with CMIP6 Simulations
Showcasing the compact Earth system model OSCAR v3.1 and its CMIP6 simulations. OSCAR is a reduced-form Earth system model calibrated to emulate complex models, focusing on radiative forcing, temperatures, precipitation, ocean heat content, aerosols, ozone, and more. Historical periods and scenarios
0 views • 15 slides
Exploring Methodological Individualism in Social Science
Critiques of invoking external agents in economics, the importance of individual behavior in explaining economic outcomes, and various interpretations of methodological individualism in social science are discussed. The focus is on explaining social phenomena through terms related to individual beli
0 views • 23 slides
Advanced Configurable Analog I/O Modules for Automation Systems
Explore a range of onboard analog I/O modules including BX10, BX18, and BX36 series, each offering high-speed discrete inputs and outputs along with analog input and output options. These modules are fully configurable with flexible voltage and current ranges. Additionally, learn about the new memor
0 views • 7 slides
Understanding Machine Learning: Types and Examples
Machine learning, as defined by Tom M. Mitchell, involves computers learning and improving from experience with respect to specific tasks and performance measures. There are various types of machine learning, including supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. Supervise
0 views • 40 slides
Enhancing GIS Outputs: Visualization, Design, and Advantages
Explore the importance of effective GIS outputs in conveying analysis results in a clear and concise manner to aid decision-makers. Learn about visualizing data, designing map outputs, and the advantages of using GIS technology for dynamic and interactive displays.
0 views • 9 slides
Communication, Dissemination, and Exploitation in Project Activities
This project involves setting up various communication channels to enhance visibility, disseminating project outputs to scientific and industry communities, exploring result exploitation with stakeholders, and maximizing impact through participation in key events. Tasks include website management, s
0 views • 13 slides
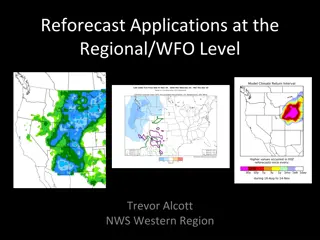
Enhancing Meteorological Forecasting Through Reforecast Applications: Challenges and Solutions
Reforecast applications at the regional/WFO level provide crucial benefits in improving model forecast accuracy and reliability, particularly for challenges like resolution in complex terrains, climatology in desert regions, and addressing model biases. Challenges include resolution limitations in m
0 views • 7 slides