Overview of Distributed Systems: Characteristics, Classification, Computation, Communication, and Fault Models
Characterizing Distributed Systems: Multiple autonomous computers with CPUs, memory, storage, and I/O paths, interconnected geographically, shared state, global invariants. Classifying Distributed Systems: Based on synchrony, communication medium, fault models like crash and Byzantine failures. Comp
9 views • 126 slides
Overview of Distributed Operating Systems
Distributed Operating Systems (DOS) manage computer resources and provide users with convenient interfaces. Unlike centralized systems, DOS runs on multiple independent CPUs and prioritizes software over hardware. It ensures transparency and fault tolerance, with a focus on software error handling.
1 views • 36 slides
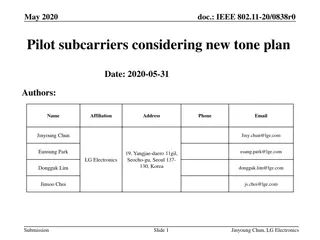
Pilot Subcarriers Optimization for IEEE 802.11-20/0838r0
The document discusses optimizing pilot subcarriers for a new tone plan in IEEE 802.11-20/0838r0. It addresses changes in RU locations, considerations for different RU combinations, and pilot subcarrier indices for various RUs. The focus is on ensuring suitable pilot subcarrier locations within the
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding CS 394B: Blockchain Systems and Distributed Consensus
This course, led by Assistant Professor Marco Canini, delves into the technical aspects of blockchain technologies, distributed consensus, and secure software engineering. Students will engage in flipped classroom-style classes and paper presentations, critiquing research papers, defending research
0 views • 65 slides
Understanding Distributed Mutual Exclusion in Operating Systems
In distributed systems, the problem of mutual exclusion arises when multiple sites/processes need to access shared resources concurrently. Unlike in single-computer systems, distributed systems lack shared memory, leading to the need for communication-based approaches rather than shared variables li
0 views • 49 slides
Understanding Parallel and Distributed Computing Systems
In parallel computing, processing elements collaborate to solve problems, while distributed systems appear as a single coherent system to users, made up of independent computers. Contemporary computing systems like mobile devices, IoT devices, and high-end gaming computers incorporate parallel and d
1 views • 11 slides
Designing Distributed and Internet Systems
Learn about the design considerations for distributed and internet systems, including file server versus client/server environments, cloud computing trends, internet standards, and system development life cycle. Explore designing systems for local area networks (LANs) and the process of creating dis
2 views • 51 slides
High-Level Thoughts on Distributed Tone Resource Unit (dRU) Design in IEEE 802.11-23/1988r2 November 2023
Various aspects of Distributed Tone Resource Unit (dRU) design in IEEE 802.11-23/1988r2, such as PSD limitations, distributed transmission regulations, application areas, and open questions are discussed in this presentation by Lin Yang from Qualcomm. Topics include tone distribution, power pooling
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Remote Method Invocation (RMI) in Distributed Systems
A distributed system involves software components on different computers communicating through message passing to achieve common goals. Organized with middleware like RMI, it allows for interactions across heterogeneous networks. RMI facilitates building distributed Java systems by enabling method i
1 views • 47 slides
Understanding Remote Method Invocation (RMI) in Distributed Systems
A distributed system involves components on different computers communicating to achieve a common goal. Middleware, like RMI, helps organize these systems. RMI allows Java objects to invoke methods on remote objects, facilitating distributed Java systems. It differs from RPC by focusing on object-or
1 views • 47 slides
Understanding Parallel and Distributed Systems in Computing
A parallel computer is a collection of processing elements that collaborate to solve problems, while a distributed system comprises independent computers appearing as a single system. Contemporary computing systems, like mobile devices and cloud platforms, utilize parallel and distributed architectu
0 views • 11 slides
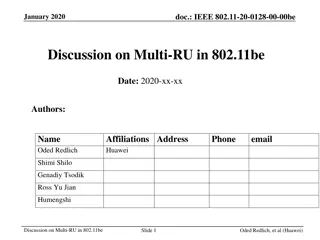
Discussion on Multi-RU Allocation in IEEE 802.11be Standard
In January 2020, a discussion took place on the allocation of multiple Resource Units (RUs) to a single Station (STA) in the IEEE 802.11be standard. The proposal suggested categorizing RUs into small and large types, avoiding aggregation across multiple 20MHz channels. It emphasized assigning a sing
2 views • 29 slides
Understanding Message Passing in Distributed Systems
Explore the key concepts of message passing in distributed systems, covering inter-process communication, desirable features like simplicity, efficiency, and reliability, different methods for information sharing, and the importance of synchronization and buffering. Dive into the intricacies of enco
0 views • 68 slides
Distributed DBMS Reliability Concepts and Measures
Distributed DBMS reliability is crucial for ensuring continuous user request processing despite system failures. This chapter delves into fundamental definitions, fault classifications, and types of faults like hard and soft failures in distributed systems. Understanding reliability concepts helps i
0 views • 58 slides
Understanding Azure Cosmos DB Billing Components and Request Units
Azure Cosmos DB billing model consists of two main components - Consumed Storage and Provisioned Throughput. You are billed based on the storage consumption and provisioned throughput. Request Units (RUs) abstract physical resources for performing requests, with specific RU costs for different types
0 views • 13 slides
SmartNIC Offloading for Distributed Applications
This presentation discusses offloading distributed applications onto SmartNICs using the iPipe framework. It explores the potential of programmable NICs to accelerate general distributed applications, characterizes multicore SmartNICs, and outlines the development and evaluation process. The study c
0 views • 31 slides
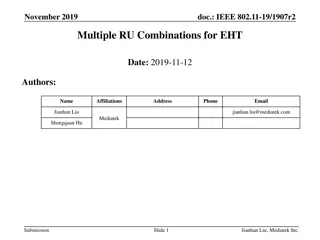
IEEE 802.11-19/1907r2 Multiple RU Combinations for EHT
11be task group approved multiple RU combinations for PPDU BW up to 160MHz. Principles outlined to limit combined RUs, focusing on spectrum use enhancement. Useful scenarios discussed for small-size RU combinations within 20MHz and 40MHz bands. Considerations highlighted regarding combining differen
0 views • 32 slides
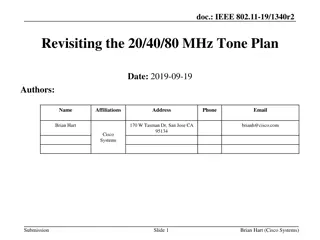
Revisiting the IEEE 802.11-19/1340r2 Tone Plan Optimization
Revisiting the tone plan optimization for IEEE 802.11-19/1340r2, addressing issues with RUs near band edges, accommodating various STA bandwidth capabilities, and the inefficiencies of non-SST 11ax STAs in different BSS scenarios. Proposals include adapting to unknown future 11ax features, minimizin
5 views • 12 slides
Multiple RU Combinations for Enhanced High Throughput (EHT) in IEEE 802.11-19/1907r0
The document discusses the introduction and design principles for multiple RU combinations in the context of IEEE 802.11-19/1907r0. It explores the considerations and useful scenarios of small-size RU combinations within specified bandwidths, emphasizing the efficiency and complexity balance in the
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Causal Consistency in Distributed Systems
This content covers the concept of causal consistency in computing systems, exploring consistency models such as Causal Linearizability and Eventual Sequential. It explains the importance of logical clocks like Lamport and vector clocks, and how they ensure order in distributed systems. The concept
0 views • 35 slides
Multi-RU Indication in Trigger Frame for IEEE 802.11
This document discusses the concept of Multi-RU (Resource Unit) allocation in trigger frames for IEEE 802.11 standards, specifically focusing on the indication methods within trigger frames for improved spectral efficiency. The proposal suggests various options for indicating multiple RUs in trigger
0 views • 14 slides
Economic Models of Consensus on Distributed Ledgers in Blockchain Technology
This study delves into Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) protocols in the realm of distributed ledgers, exploring the complexities of achieving consensus in trusted adversarial environments. The research examines the classic problem in computer science where distributed nodes communicate to reach agre
0 views • 34 slides
Distributed Algorithms for Leader Election in Anonymous Systems
Distributed algorithms play a crucial role in leader election within anonymous systems where nodes lack unique identifiers. The content discusses the challenges and impossibility results of deterministic leader election in such systems. It explains synchronous and asynchronous distributed algorithms
2 views • 11 slides
Overview of Distributed Systems, RAID, Lustre, MogileFS, and HDFS
Distributed systems encompass a range of technologies aimed at improving storage efficiency and reliability. This includes RAID (Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks) strategies such as RAID levels, Lustre Linux Cluster for high-performance clusters, MogileFS for fast content delivery, and HDFS (Had
0 views • 23 slides
Distributed Software Engineering Overview
Distributed software engineering plays a crucial role in modern enterprise computing systems where large computer-based systems are distributed over multiple computers for improved performance, fault tolerance, and scalability. This involves resource sharing, openness, concurrency, and fault toleran
0 views • 66 slides
Challenges in Detecting and Characterizing Failures in Distributed Web Applications
The final examination presented by Fahad A. Arshad at Purdue University in 2014 delves into the complexities of failure characterization and error detection in distributed web applications. The presentation highlights the reasons behind failures, such as limited testing and high developer turnover r
0 views • 53 slides
Google Spanner: A Distributed Multiversion Database Overview
Represented at OSDI 2012 by Wilson Hsieh, Google Spanner is a globally distributed database system that offers general-purpose transactions and SQL query support. It features lock-free distributed read transactions, ensuring external consistency of distributed transactions. Spanner enables property
0 views • 27 slides
Understanding the CAP Theorem in Distributed Systems
The CAP Theorem, as discussed by Seth Gilbert and Nancy A. Lynch, highlights the tradeoffs between Consistency, Availability, and Partition Tolerance in distributed systems. It explains how a distributed service cannot provide all three aspects simultaneously, leading to practical compromises and re
0 views • 28 slides
Understanding Distributed Hash Table (DHT) in Distributed Systems
In this lecture, Mohammad Hammoud discusses the concept of Distributed Hash Tables (DHT) in distributed systems, focusing on key aspects such as classes of naming, Chord DHT, node entities, key resolution algorithms, and the key resolution process in Chord. The session covers various components of D
0 views • 35 slides
Distributed Database Management and Transactions Overview
Explore the world of distributed database management and transactions with a focus on topics such as geo-distributed nature, replication, isolation among transactions, transaction recovery, and low-latency maintenance. Understand concepts like serializability, hops, and sequence number vectors in ma
0 views • 17 slides
Distributed Computing Systems Project: Distributed Shell Implementation
Explore the concept of a Distributed Shell in the realm of distributed computing systems, where commands can be executed on remote machines with results returned to users. The project involves building a client-server setup for a Distributed Shell, incorporating functionalities like authentication,
0 views • 14 slides
Overview of Ceph Distributed File System
Ceph is a scalable, high-performance distributed file system designed for excellent performance, reliability, and scalability in very large systems. It employs innovative strategies like distributed dynamic metadata management, pseudo-random data distribution, and decoupling data and metadata tasks
0 views • 42 slides
Overview of Ceph: A Scalable Distributed File System
Ceph is a high-performance distributed file system known for its excellent performance, reliability, and scalability. It decouples metadata and data operations, leverages OSD intelligence for complexity distribution, and utilizes adaptive metadata cluster architecture. Ceph ensures the separation of
0 views • 23 slides
Distributed Transaction Management in CSCI 5533 Course
Exploring transaction concepts and models in distributed systems, Team 5 comprising Dedeepya, Dodla, Ehtheshamuddin, and Hari Kishore under the guidance of Dr. Andrew Yang delve into the intricacies of distributed transaction management in CSCI 5533 Distributed Information Systems.
0 views • 56 slides
Concurrency Control and Coordinator Election in Distributed Systems
This content delves into the key concepts of concurrency control and coordinator election in distributed systems. It covers classical concurrency control mechanisms like Semaphores, Mutexes, and Monitors, and explores the challenges and goals of distributed mutual exclusion. Various approaches such
0 views • 48 slides
Quantum Distributed Proofs for Replicated Data
This research explores Quantum Distributed Computing protocols for tasks like leader election, Byzantine agreement, and more. It introduces Quantum dMA protocols for verifying equality of replicated data on a network without shared randomness. The study discusses the need for efficient protocols wit
0 views • 28 slides
IEEE 802.11-16/0592r0: Follow-up on Unused UL OFDMA RUs
In May 2016, a presentation by Stéphane Baron and team from Canon addressed the issue of unused Random Units (RUs) in UL OFDMA transmission in IEEE 802.11 standards. The presentation covers the consequences, simulation results showing significant unused RUs, and a proposed solution of random RUs in
0 views • 8 slides
IEEE 802.11-23/1953r0 Two-Dimensional Resource Allocation (UL OFDMA)
Introducing a novel approach for uplink transmissions in UHR to achieve low-latency communication. The document discusses UL OFDMA in detail, emphasizing the use of a two-dimensional resource unit. Key topics covered include UL MU operation, UL OFDMA-based random access, and allocation of RUs for ra
0 views • 16 slides
Discussion on Distributed RUs (DRUs) in IEEE 802.11-24/0332r0
The document discusses Distributed RUs (DRUs) as a solution to work around 6 GHz regulations limiting transmit PSD per MHz. DRU energizes a few subcarriers per MHz to improve link budget by 11 dB at the cost of data rate scaling. It also examines the problem of throughput degradation in DRU with ins
0 views • 9 slides
Discussion on Improving Transmission Efficiency in IEEE 802.11 TWT Mechanism
This document proposes enhancements to the IEEE 802.11 TWT mechanism to address issues related to random access Resource Units (RU) utilization. By defining a mechanism to optimize RU allocation for TWT scheduled STAs, the proposal aims to improve transmission efficiency and power saving, particular
0 views • 11 slides