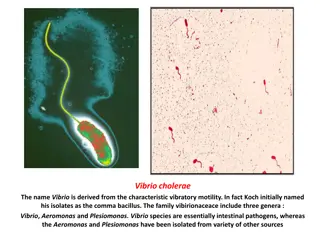
Understanding Vibrio and Related Organisms in Medical Bacteriology
Vibrio, Aeromonas, and Plesiomonas are gram-negative bacilli commonly found in water sources, causing gastrointestinal diseases. They exhibit similarities to Enterobacteriaceae but with distinct characteristics such as polar flagella and being oxidase-positive. Vibrios like V. cholerae are crucial h
1 views • 25 slides
Microbiology Lab Tests for Identifying Bacterial Pathogens
Learn about key biochemical tests like the Coagulase Test, Catalase Test, and Oxidase Test used in medical microbiology to identify pathogenic bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus. Understand the methods, significance, and interpretation of results for each test.
4 views • 17 slides
Overview of Vibrio cholerae: Characteristics and Identification
Vibrio cholerae is a gram-negative, curved rod bacterium known for causing cholera. Its distinctive features include polar flagellum motility, oxidase-positive nature, and resistance to inhibitory substances. Various culture media are used for its isolation and growth, such as transport, routine, an
0 views • 8 slides
Quantitative Estimation of Glucose by Enzymatic Method in Blood Samples
Estimation of blood glucose levels is crucial for diagnosing and managing conditions like diabetes mellitus. This practical involves using the enzymatic method with glucose oxidase to quantitatively determine glucose levels in serum. The enzymatic reaction converts glucose to gluconic acid and hydro
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Enzymatic Browning in Food Chemistry
Enzymatic browning is a chemical reaction that causes fruits and vegetables to turn brown when exposed to oxygen. This process, driven by enzymes like polyphenol oxidase (PPO), leads to the formation of brown pigments called melanins. Discover how enzymatic browning happens, its impact on various fo
0 views • 20 slides
Microbiology Biochemical Tests for Bacterial Identification
Learn about important biochemical tests used in medical microbiology, including the Coagulase test for Staphylococcus aureus, the Catalase test for enzyme detection, and the Oxidase test for electron transport chain identification. Detailed methods and result interpretations are provided for each te
0 views • 17 slides
Cholera Diagnosis and Control Methods Overview
Cholera diagnosis involves various laboratory tests such as specimen analysis, smears, and cultures. Slide agglutination tests and the oxidase test can also aid in the identification of Vibrio cholerae bacteria. Understanding these diagnostic methods is crucial for effective control and management o
0 views • 14 slides
Overview of Enterobacteriaceae Family and Their Antigenic Structure
The Enterobacteriaceae family comprises a diverse group of gram-negative rods commonly found in the gut of humans and animals, known for causing various diseases. Key members include Escherichia coli, Shigella, Salmonella, Klebsiella, and more. They are facultative anaerobes, ferment glucose, lack c
0 views • 48 slides
Cyanide's Impact on Respiration Through Enzyme Inhibition
Cyanide, a noncompetitive inhibitor of the enzyme cytochrome c oxidase, disrupts electron transport in respiration by binding to the iron cofactor and blocking electron transfer to oxygen. This lethal effect was utilized in gas chambers during WWII, underscoring the crucial role of enzyme function i
0 views • 7 slides
Factors Affecting Polyphenol Oxidase Activity in Enzyme Reaction
Polyphenol oxidase (PPO) is a copper-containing enzyme with an optimal pH of 6.7 that catalyzes the oxidation of phenols, leading to color changes like browning in fruits and potatoes. This experiment aims to demonstrate PPO activity, its chemical nature, substrate specificity, and the effects of te
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Drug Metabolism and Excretion in Pharmacology
Drug metabolism involves the biotransformation of pharmaceutical substances in the body, primarily in the liver, to facilitate their elimination. This process helps convert drugs into less active forms for enhanced elimination through various reactions in Phase I and Phase II metabolism. Factors suc
0 views • 20 slides
Overview of Neisseria Species: Characteristics, Pathogenicity, and Laboratory Diagnosis
Neisseria species are Gram-negative diplococci known for pathogens like N. gonorrhoeae causing gonorrhea and N. meningitidis causing meningitis. They are aerobic to facultatively anaerobic, oxidase-positive, non-motile, and encapsulated cocci. N. gonorrhoeae is fastidious, requiring increased CO2 te
0 views • 20 slides