Understanding Sampling Methods in Social Research
Sampling in social research involves selecting a subset of a population to make inferences about the whole. It helps in saving time and money, ensures accuracy in measurements, and allows estimation of population characteristics. The key principles of sampling include systematic selection, clear def
1 views • 19 slides
Understanding Sampling Methods in Statistical Analysis
Sampling is a crucial process in statistical analysis where observations are taken from a larger population. Different sampling techniques are used based on the analysis being performed. Sampling methods help in studying populations when studying the entire population is not feasible. There are two
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding and Avoiding Bias in Evidence-Based Responses
Recognizing bias in oneself and others is crucial when collecting evidence. Different types of bias, such as confirmation bias, can influence decisions and behaviors significantly. By exploring our own thinking and accessing curated resources to learn about bias, we can develop a deeper understandin
1 views • 14 slides
Recognizing Hidden Bias in the Workplace
In the workplace, hidden bias, also known as implicit bias, can significantly impact hiring, employment decisions, and overall workplace dynamics. Deloitte's 2019 State of Inclusion Survey revealed that a substantial percentage of workers experienced bias at least monthly. Hidden biases can be based
3 views • 18 slides
Sampling Under the RRF - General Principles and Methods
Sampling under the RRF is essential for the Commission to ensure reasonable assurance of fulfillment of numerical milestones or targets. The approach involves statistical risk-based random sampling with specific thresholds and considerations for different types of milestones. Various statistical tab
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding Non-Probability Sampling Methods
Non-probability sampling methods involve selecting samples based on subjective judgment rather than random selection. Types include convenience sampling, quota sampling, judgmental (purposive) sampling, and snowball sampling. Convenience sampling picks easily available samples, quota sampling select
2 views • 7 slides
Overcoming Unconscious Bias in Talent Acquisition Process
Overcoming Unconscious Bias in Talent Acquisition Process emphasizes the importance of addressing unconscious bias in hiring practices through awareness and control. The content delves into defining unconscious bias, its impact on diversity, examples, and strategies for managing bias. The University
0 views • 19 slides
Systematic Analysis of Real Samples in Analytical Chemistry
This analysis covers the systematic process involved in analyzing real samples, including sampling, sample preservation, and sample preparation. It discusses the importance of accurate sampling in obtaining information about various substances, such as solids, liquids, gases, and biological material
0 views • 54 slides
Understanding and Utilizing Bias in Legal Proceedings
Exploring the complexities of bias in legal settings, this content provides insights on identifying, addressing, and leveraging bias in litigation. From defining various forms of bias to strategies for cross-examination and case presentation, it equips legal professionals with practical knowledge to
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Sampling Plans in Statistical Analysis
Sampling is vital for statistical analysis, with sampling plans detailing objectives, target populations, operational procedures, and statistical tools. Different sampling methods like judgmental, convenience, and probabilistic sampling are used to select samples. Estimation involves assessing unkno
1 views • 36 slides
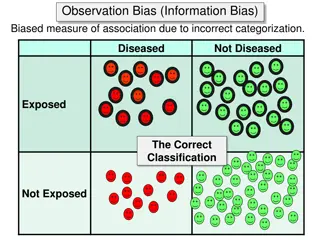
Types of Bias in Epidemiological Studies
Bias in epidemiological studies can arise from misclassification of observations and exposures, leading to incorrect associations between variables. Observation bias, misclassification bias, and non-differential misclassification can impact the accuracy of study results, either minimizing difference
1 views • 11 slides
Understanding Sampling Methods and Errors in Research
Sampling is crucial in research to draw conclusions about a population. Various methods like simple random sampling, stratified sampling, and systematic sampling help in selecting representative samples. Sampling error arises due to differences between sample and population values, while bias leads
0 views • 12 slides
Fundamentals of Food Sampling and Analysis
Discover the key methods and procedures for sampling, transportation, and storage of environmental parameters, focusing on food sampling and analysis. Explore the importance of representative samples, quality analysis results, and risks associated with sampling. Learn about homogeneous vs. heterogen
5 views • 36 slides
Understanding Implicit Bias in Medical Education
Delve into the origins, forms, and manifestations of bias in clinical and medical education settings. Learn strategies to mitigate and address bias through a detailed exploration of terms like System 1 and System 2 thinking, implicit bias, race/racism, sexism, microaggressions, and more. Gain insigh
6 views • 27 slides
Understanding Bias in Sampling and Surveys
Bias in sampling and surveys can arise from undercoverage, nonresponse, and response bias. Even when samples are randomly selected, various factors can lead to inaccurate results. Researchers need to be aware of these biases and take steps to minimize them, such as testing surveys before full deploy
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Transistor Bias Circuits for Linear Amplification
Transistor bias circuits play a crucial role in setting the DC operating point for proper linear amplification. A well-biased transistor ensures the signal variations at the input are accurately reproduced at the output without distortion. Various biasing methods such as Voltage-Divider Bias, Emitte
0 views • 7 slides
Understanding Sampling and Signal Processing Fundamentals
Sampling plays a crucial role in converting continuous-time signals into discrete-time signals for processing. This lecture covers periodic sampling, ideal sampling, Fourier transforms, Nyquist-Shannon sampling, and the processing of band-limited signals. It delves into the relationship between peri
1 views • 60 slides
Understanding Biases in Sampling Methods
Statistical studies rely on samples to draw conclusions about populations, but the method of sampling can introduce biases. This text discusses convenience sampling, voluntary response sampling, random sampling, and the implications of biased sampling methods on study results. It highlights how bias
1 views • 12 slides
Managing Reporting Bias in Systematic Reviews - Strategies and Consequences
Reporting bias poses a significant threat to the accuracy of systematic reviews, with publication bias affecting up to 50% of trials. This bias distorts treatment effect estimates, leading to exaggerated outcomes. Strategies to mitigate reporting bias include searching bibliographical databases, exp
1 views • 17 slides
Guide to Environmental Surface Sampling Techniques
Understanding the importance of environmental surface sampling is crucial for ensuring hygiene and safety. This guide covers key aspects such as pre-sampling considerations, aseptic techniques, major sampling methods like RODAC plate, swab, and wipe methods, along with detailed procedures for each m
1 views • 16 slides
Lead Dust Wipe Sampling Techniques and Guidelines
This resource provides valuable information on lead dust wipe sampling techniques for Lead Dust Sampling Technicians. It covers the objectives, measuring lead dust, sampling strategy, sampling locations based on EPA RRP Rule, and HUD clearance regulations. Techniques for taking dust wipe samples, id
2 views • 41 slides
Comprehensive Guidelines for Meth Residue Sampling by Local Health Departments
This detailed guide outlines the procedures and protocols for meth residue sampling conducted by local health departments. It covers the reasons for sampling, the importance of qualified inspectors, testing methodologies, sampling kits assembly, and more. Key points include when and why sampling is
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Sampling in Survey Research
This content covers essential concepts of survey research, statistics, and sampling methods. It delves into elements of the sampling problem, technical terms, and how to select a sample for surveys. The discussions revolve around population parameters, sampling procedures, and the control of informa
1 views • 39 slides
Understanding Sampling in Social Research Methods
Sampling in social research involves selecting a portion of a population to draw conclusions about the entire group. It helps save time, money, and allows for accurate measurements. The key principles of sampling include systematic selection, clear definition of sample units, independence of units,
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Non-Probability Sampling Methods
Non-probability sampling involves selecting samples based on subjective judgment rather than random selection, leading to a lack of equal chances for all population members to participate. Various types include convenience sampling, quota sampling, judgmental sampling, and snowball sampling. Conveni
1 views • 7 slides
Understanding Sampling in Artificial Intelligence: An Overview
Exploring the concept of sampling in artificial intelligence, particularly in the context of Bayesian networks. Sampling involves obtaining samples from unknown distributions for various purposes like learning, inference, and prediction. Different sampling methods and their application in Bayesian n
2 views • 29 slides
Approximate Inference in Bayes Nets: Random vs. Rejection Sampling
Approximate inference methods in Bayes nets, such as random and rejection sampling, utilize Monte Carlo algorithms for stochastic sampling to estimate complex probabilities. Random sampling involves sampling in topological order, while rejection sampling generates samples from hard-to-sample distrib
0 views • 9 slides
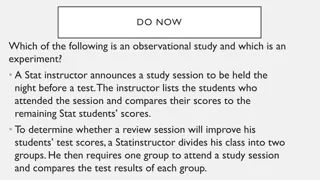
Understanding Observational Studies vs. Experiments in Statistical Analysis
Explore the distinction between observational studies and experiments in statistics through practical examples like a Stat instructor evaluating a review session's impact on test scores. Learn about sampling methods, bias avoidance, and the implications of statistical study design. Discover how anal
1 views • 12 slides
Understanding Sampling Methods in Business Analytics
Sampling plays a crucial role in estimating proportions and making informed decisions in business analytics. From polling to estimating proportions, this class explores sampling techniques, sample size determination, and potential biases. Learn about choosing a sample size, stratified and cluster sa
2 views • 23 slides
Understanding Transition Bias and Substitution Models in Genetics
Transition bias and substitution models, explored by Xuhua Xia, delve into the concepts of transitions and transversions in genetic mutations, the causes of transition bias, the ubiquitous nature of transition bias in invertebrate and vertebrate genes, the mitochondrial genetic code, and RNA seconda
1 views • 25 slides
Understanding Experimental Design and Bias in Statistics
Explore key concepts in statistics such as observational studies, experiments, bias, and sampling methods. Delve into the difference between observational studies and experiments, understand the impact of bias in research, and learn about sampling techniques like simple random sampling and stratifie
0 views • 22 slides
Addressing Bias-Related Incidents at Concordia University
The report discusses bias reporting at Concordia University, highlighting the importance of understanding and addressing bias-related incidents. It covers examples of bias, distinction between bias incidents and hate crimes, and strategies for response. Presenters from the Office of Multicultural En
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Non-Probability Sampling Methods
Non-probability sampling involves selecting samples based on subjective judgement rather than random selection. This method may not give all population members an equal chance to participate. Types include convenience sampling, quota sampling, judgemental sampling, and snowball sampling.
0 views • 7 slides
Understanding Non-Probability Sampling Techniques in Nursing Research
Non-probability sampling in nursing research involves selecting samples subjectively rather than randomly. This sampling method carries a higher risk of bias and limits statistical inference about the entire population. Five main types include convenience, purposive, quota, snowball, and voluntary r
0 views • 30 slides
Understanding Implicit Bias: Exploring Bias, Stereotypes, and Discrimination
Explore the concept of implicit bias through discussions about prior knowledge, feelings pre and post taking implicit association tests, and how this awareness can be applied beneficially in personal and classroom settings. Definitions of implicit bias, stereotypes, prejudice, and discrimination are
0 views • 21 slides
Understanding Cost Overruns in Projects: Systematic Bias vs. Selection Bias
Cost overruns in projects can be attributed to systematic bias, like optimism bias and strategic misrepresentation, or selection bias where projects with low estimated costs are more likely to be selected leading to underestimation. Mitigating these biases is crucial for accurate project budgeting a
0 views • 21 slides
Understanding the Importance of Sampling in Quality Control
Sampling plays a crucial role in quality control by providing information about a population based on characteristics observed in a sample. Random sampling helps study population characteristics without bias, ensuring that each possible sample has an equal probability of being drawn. Various methods
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding Experimenter Bias in Research Studies
Experimenter bias occurs when researchers introduce their own biases into an experiment, potentially impacting the outcome. This bias can manifest in various ways, such as manipulating results or selecting participants who confirm preconceived notions. Through examples in studies about toddler sleep
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding Sampling: Importance, Process, and Errors Explained
This content delves into the world of sampling, exploring why sampling is crucial, the sampling process involving defining populations and calculating sample sizes, and the distinction between non-sampling and sampling errors. It covers the significance of representative samples, common errors in sa
0 views • 15 slides
Investigating Bias in Newspaper Articles through Natural Language Processing
The project, mentored by Jason Cho and advised by Professor Eric Meyer, focuses on automatic bias detection in newspaper articles. It involves recognizing similar article topics and detecting bias using tools like OpenNLP and Python NLTK. The endeavor aims to uncover words correlated with bias and a
0 views • 5 slides