The Role of Sunlight, Ozone, and Plant Life in Earth's Atmosphere
Sunlight plays a crucial role in the formation of ozone from oxygen, leading to the protection of plant life against harmful UV radiation. The ozone produced by sunlight helps in the photosynthesis process of plants, which in turn release oxygen, absorb CO2, and contribute to the overall balance of
7 views • 23 slides
Understanding Atmosphere Composition and Structure in Climatology
The study of climatology, focusing on the atmosphere, is presented by Dr. Banashree Saikia, covering topics such as atmospheric composition, insolation, temperature variations, atmospheric pressure, wind systems, atmospheric moisture, climatic classification, cyclones, and monsoons. The atmosphere,
1 views • 9 slides
Understanding Geopotential and Geopotential Height in Atmospheric Thermodynamics
Explore the concept of geopotential and geopotential height in atmospheric sciences, focusing on their significance in understanding gravitational and centrifugal forces on Earth. Learn about the definition, calculation, and applications of geopotential height in relation to atmospheric properties a
1 views • 14 slides
Understanding Atmospheric Moisture in Physical Geography
Atmospheric moisture, in the form of water vapor, liquid water, and ice, plays a crucial role in shaping weather and climate. This course delves into the dynamics of atmospheric moisture, including its distribution, effects on weather patterns, and impact on various climatic factors such as precipit
0 views • 7 slides
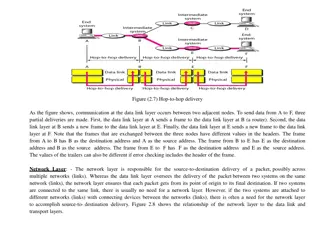
Understanding Communication Layers in Computer Networks
Communication in computer networks is facilitated through different layers such as the data link, network, and transport layers. Each layer has specific responsibilities in ensuring data delivery from one point to another. The data link layer handles communication between adjacent nodes, the network
3 views • 7 slides
Understanding OSI Reference Model Layers
The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model consists of 7 layers, each with specific functions in network communication. From the Application layer handling user services to the Physical layer dealing with data transmission, learn about the responsibilities and interactions of these layers in netwo
0 views • 26 slides
Understanding Atmospheric Thickness and Its Applications
Atmospheric thickness refers to the difference in geopotential height between two pressure surfaces, which is dependent on the mean virtual temperature of the layer in between. This concept plays a key role in determining temperature gradients, identifying fronts, and aiding in weather forecasting,
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding OSI Model and TCP/IP Protocol Suite in Computer Networking
This chapter explores the OSI model and TCP/IP protocol suite, delving into protocol layers, addressing mechanisms, and network components. It highlights the interface between layers, functions of each layer in the OSI model, and compares TCP/IP protocol suite layers with OSI model layers. The discu
0 views • 30 slides
Understanding Synoptic Meteorology: A Comprehensive Overview
Synoptic meteorology delves into various aspects of atmospheric sciences, encompassing scales of atmospheric motion, weather maps, air masses, fronts, jet streams, and more. Through the study of synoptic meteorology, meteorologists gain insights into interpreting the state of the troposphere and for
1 views • 17 slides
Understanding Atmospheric Pressure Variations at Different Altitudes
Atmospheric pressure varies with altitude due to the weight of the air column above. This activity explores how Otto von Guericke's experiments with vacuum systems demonstrate the power of air pressure. Theoretical concepts of atmospheric pressure are discussed, highlighting its relation to gravity
0 views • 28 slides
Understanding the Layers of the Ionosphere
Explore the layers of the ionosphere including the D, E, Es, and F layers and how they impact radio wave propagation. Discover how solar activity affects ionization levels and skip distances, offering insights into long-distance communication potential. Learn about the influence of solar radiation o
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Gases in the Earth's Atmosphere
Explore the composition and layers of the Earth's atmosphere, including the significance of gases like nitrogen, oxygen, water vapor, and carbon dioxide. Learn how human activities impact atmospheric composition and how changes in temperature and pressure affect weather predictions. Discover the rol
0 views • 13 slides
Cutting-Edge Atmospheric Chemistry Modeling Research at Barcelona Supercomputing Center
Conducted by the Atmospheric Composition Group at Barcelona Supercomputing Center, this cutting-edge research focuses on atmospheric chemistry modeling using advanced tools and frameworks like HERMESv3 and MONARCH. The team's approach integrates various modules to study complex processes influencing
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding Fluid Statics and Atmospheric Pressure Measurements
Exploring the concept of fluid statics, this content delves into topics such as how atmospheric pressure is measured, buoyancy, and why a steel boat can float. It covers the measurement of pressure, the relationship between pressure and depth in fluids, and demonstrations showcasing these principles
0 views • 24 slides
Overview of Low-Cost Sensors for Atmospheric Composition Measurement
This publication provides an insightful overview of low-cost sensors for measuring atmospheric composition, covering topics like sensor technologies, applications in atmospheric sciences and air quality management, and evaluation methods. It emphasizes the importance of not only the technical perfor
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Atmospheric Circulation on Earth
An atmospheric circulation driven by temperature differences between the equator and poles influences global weather patterns. The sun's changing angle throughout the year results in various pressure areas and the formation of large circulation cells. The main effects include the transport of humidi
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding the Planetary Boundary Layer in Atmospheric Science
The Planetary Boundary Layer (PBL) plays a crucial role in atmospheric dynamics, divided into surface, mixed, stable, and residual layers. During the day, the mixed layer experiences convective motions due to surface heating, while the stable layer dominates during the night. Understanding these lay
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Earth's Atmosphere: A Detailed Overview
The Earth's atmosphere is a vital layer of gases that encircles our planet, providing the necessary conditions for life to thrive. It consists of several distinct layers, each with unique characteristics and functions. From the troposphere closest to the surface to the thermosphere extending to grea
0 views • 29 slides
Mastering Motion Guide Layers for Advanced Animation
Dive into the world of Motion Guide Layers to control object movement in animation projects. Learn how to create, use, and manipulate Motion Guide Layers effectively, along with tips on leveraging mask layers for spotlight effects and transitions. Discover techniques for grouping objects and creatin
0 views • 16 slides
NSF Atmospheric Chemistry Program Overview
The NSF Atmospheric Chemistry Program aims to characterize the chemical composition of the atmosphere, understand chemical processes, quantify fluxes of chemical substances, study natural and anthropogenic causes of variability, and assess impacts on climate. The program supports research through pe
0 views • 6 slides
Understanding Atmospheric Chemistry Measurements and Methods
Explore the various types of atmospheric chemistry measurements, including research vs. monitoring, gas phase species, satellite vs. in situ observations, and spectroscopy and chromatography methods. Discover how researchers and regulatory bodies use different techniques to study and monitor air qua
0 views • 34 slides
Understanding Layering in Wireless Networks
This content delves into the concept of layering in wireless networks, highlighting the motivation behind layering, the Internet's approach to avoiding reimplementation for each underlying medium, the role of intermediate layers in providing abstractions, properties of network layers, and the functi
0 views • 53 slides
Understanding Atmospheric Composition and Structure
The presentation covers fundamental concepts related to the Earth's atmosphere, including its composition, origin of oxygen, dry and moist layers, standard atmosphere layers, and temperature variations. Key topics discussed include the primordial atmosphere, atmospheric constituents, water vapor dis
0 views • 58 slides
Exploring Layers of Earth's Atmosphere
Earth's atmosphere consists of five major layers, each with unique properties and temperature changes with altitude. The troposphere, closest to the Earth's surface, experiences a temperature decrease with altitude due to heat from the sun and Earth's surface. Learn about the properties of the tropo
0 views • 26 slides
Understanding Atmospheric Thermodynamics and Environmental Lapse Rate
Explore the concepts of atmospheric thermodynamics including the Parcel Method, Environmental Lapse Rate, and Conditionally Unstable Atmosphere. Dive into the details of how air parcels behave in different atmospheric conditions and understand the significance of temperature changes in the atmospher
0 views • 27 slides
GEOS-Chem Atmospheric Chemistry Model Overview
GEOS-Chem, developed by Daniel J. Jacob at Harvard University, is a global model of atmospheric composition used to understand human and natural influences on the environment. The model addresses various atmospheric chemistry issues on different scales, from local to global, and is regularly updated
0 views • 19 slides
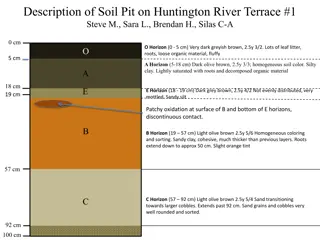
Detailed Descriptions of Soil Pits on Huntington River Terrace
The soil pits on Huntington River Terrace provide detailed insights into the soil composition at different depths. Terrace #1 exhibits dark greyish-brown to light olive-brown layers with varying textures, while Terrace #2 showcases well-sorted clay and gravel transitions. Terrace #3 presents a mixtu
0 views • 4 slides
Understanding Atmospheric Stability and Adiabatic Processes
Atmospheric stability is crucial in determining weather conditions. Different processes such as adiabatic cooling play a significant role in the vertical movement of air masses. Understanding the environmental lapse rate, moist and dry adiabatic rates, and the concept of conditional instability help
0 views • 4 slides
Understanding Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) in Depth
CNN, a type of neural network, comprises convolutional, subsampling, and fully connected layers achieving state-of-the-art results in tasks like handwritten digit recognition. CNN is specialized for image input data but can be tricky to train with large-scale datasets due to the complexity of replic
0 views • 22 slides
Understanding Atmospheric Pressure, Wind Variations, and Humidity in Weather Systems
The atmosphere is composed of various elements like gaseous molecules, water vapor, and dust particles. Key weather variables include atmospheric pressure, temperature, humidity, wind, cloud cover, and precipitation. Atmospheric pressure is influenced by the weight of air above a point, with average
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding OSI Model and TCP/IP Protocol Suite in Computer Networking
This content delves into the OSI model and TCP/IP protocol suite, highlighting the protocol layers, addressing mechanisms, and communication scenarios. It explores the functions of each layer, the interface between layers, and compares the TCP/IP layers with the OSI model. Through examples and illus
0 views • 46 slides
The DC and AC global atmospheric electric circuits as central tenets in Earth system science today
The presentation at the EGU General Assembly highlighted the significance of DC and AC global atmospheric electric circuits in Earth system science. Key references from 2007 to 2018 underscore the evolving research in this field, exploring the interconnectedness between the space environment and the
0 views • 23 slides
Journey to the Earth's Layers
The Earth's structure consists of four main layers: the crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core. The crust is the thin, rocky layer we see on the surface, while the mantle is a solid layer that flows like a viscous liquid. The outer core is a hot, melted layer of iron and nickel, and the inner cor
0 views • 10 slides
Journey to the Center of the Earth: Unveiling the Layers
Delve into the depths of the Earth with Dr. A.V. Tejankar to explore the three main layers - Crust, Mantle, and Core. Discover how the Earth's composition and physical properties vary across these layers, resembling the layers of an egg. Uncover the secrets of the Earth's interior, from the thin but
0 views • 15 slides
Exploring Earth's Interior: Layers, Structure, and Seismic Waves
Explore the dynamic layers of Earth's interior, from its three major layers formed by gravity and chemical segregation to mineral and phase changes in the mantle. Discover how seismic waves provide insights into the planet's composition as they interact with different layers, reflecting and refracti
0 views • 50 slides
Addressing the Gap Between Graduates' Skills and Employers' Expectations in Atmospheric Geosciences
The article discusses the skills gap in the atmospheric geosciences field, highlighting key technical and communication skills needed by graduates and postgrads. It explores strategies to bridge this gap through surveys, creative solutions, and innovative approaches like updating degree requirements
0 views • 5 slides
Understanding Tropical Cyclones and Layers of the Atmosphere
Tropical cyclones are warm-core low-pressure systems that form over oceans with high sea surface temperatures. The Philippines is prone to these cyclones, leading to heavy rains, flooding, and strong winds. The layers of the atmosphere, from the exosphere to the troposphere, play crucial roles in sh
0 views • 7 slides
Understanding Protocol Layers in Computer Networking
Explore the concept of protocol layers in computer networks for organizing the structure of complex systems. Learn about the organization of network functionality similar to air travel processes and the benefits of layering in dealing with complex systems. Delve into the Internet Protocol Stack, hig
0 views • 29 slides
Analysis of Atmospheric Parameters and Transmission at OHP in 2018
This analysis focuses on the atmospheric parameters and transmission at the Observatoire de Haute-Provence (OHP) during 2018, with a specific emphasis on distinguishing between typical winter and summer conditions. The study utilizes MERRA2 data from January to August to examine pressure, precipitab
0 views • 16 slides
Atmospheric Correction Techniques for Satellite Image Enhancement
Atmospheric correction is essential for improving the quality of Remote Sensing images captured by satellites. This process involves correcting for the effects of atmospheric gases such as scattering and absorption on the measured Top-of-Atmosphere (TOA) reflectance. Techniques like molecular correc
0 views • 8 slides