Understanding the Distinctive Features of Human Language
Human language is characterized by distinctive features such as the use of sound signals, arbitrariness, the need for learning, duality, and displacement. These intrinsic features set human language apart from other communication systems, allowing for complex and diverse forms of expression.
3 views • 12 slides
Understanding Administrative Law: Scope and Nature
Administrative law is a branch of public law that governs the relationship between the state and its citizens, regulating how power is exercised by the executive branch and administrative agencies. It sets legal limits to ensure protection against abuse of power and arbitrariness, focusing on the or
0 views • 26 slides
Uniqueness of Human Language and Communication Contrasted with Animal Communication
Human language possesses unique properties such as reflexivity, displacement, and arbitrariness, setting it apart from animal communication. These distinctions enable humans to communicate abstract concepts, discuss past and future events, and use arbitrary linguistic forms. The contrast between hum
1 views • 17 slides
Understanding Linguistic Concepts and Unique Aspects of Human Language
Exploring the fundamental concepts of linguistics such as phonology, morphology, and syntax, along with the distinction between prescriptive and descriptive grammar. Delving into different kinds of ungrammaticalities and the properties that make human language unique, including displacement, arbitra
0 views • 30 slides
Exploration of Substance-Free Phonology and Phonological Theory
This text delves into the concept of substance-free phonology, discussing the arbitrariness of phonological items, the distinction between phonologically meaningful and meaningless items, and the relationship between phonology and phonetics. It also explores the role of sonority in phonological theo
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding the Distinctive Features of Human Language
Human language possesses distinctive features such as the use of sound signals, arbitrariness, displacement, duality, the need for learning, creativity, patterning of units, and structure dependence. These features set human language apart from other communication systems, emphasizing its complexity
0 views • 19 slides
How Human Language Differs from Animal Communication
Human language distinguishes itself from animal communication through properties like displacement, arbitrariness, and productivity. Displacement enables discussing abstract concepts, arbitrariness shows the non-literal connection between words and meanings, and productivity allows for endless expre
0 views • 21 slides
Understanding Structuralism in Linguistics: An Overview
Structuralism emerged as a dominant approach in linguistic studies from the 1920s to the 1960s, led by figures like Ferdinand de Saussure. This philosophical perspective focused on the study of language as a stable system of signs, emphasizing the interrelation of mental representations of sounds an
1 views • 28 slides
Understanding Language Properties and Definitions
Language is defined by its unique properties such as rapid fading, interchangeability, feedback, semanticity, arbitrariness, discreteness, displacement, productivity, cultural transmission, duality, prevarication, reflexiveness, and learnability. These properties help distinguish human language from
0 views • 19 slides
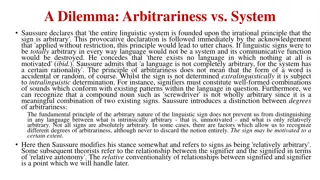
The Principle of Arbitrariness in Linguistic Signs: Saussure's Insight
Saussure's declaration on the arbitrariness of linguistic signs is thought-provoking, emphasizing that while signs are arbitrary, complete arbitrariness would lead to chaos. He distinguishes between degrees of arbitrariness and acknowledges that signs are not entirely arbitrary, being subject to lin
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding the Duty to Act in the Public Interest in Legal Context
The concept of the duty to act in the public interest, as applied in legal settings, involves delegated responsibility by the public to regulatory bodies or decision-makers. This duty entails exercising judgment and discretion founded on a cultural consensus and public trust. Despite limited guidanc
0 views • 26 slides