The Fascinating World of Algae and Protists
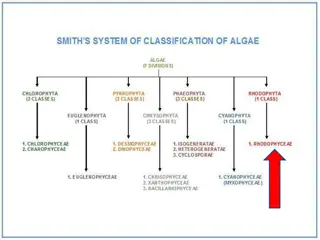
Algae, diatoms, dinoflagellates, euglenoids, and red algae are diverse plant-like protists crucial for Earth's ecosystems. They range from unicellular to multicellular forms, contributing significantly to oxygen production and food chains. While some like red algae thrive in deep ocean waters, others like dinoflagellates can cause red tides with harmful toxins. Understanding these organisms sheds light on their ecological importance and impact on aquatic life.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Algae: Plantlike Protists Life Science - Mr. Hooper - January 2013
The Algae: Plantlike Protists Algae are autotrophs. Algae may be unicellular or multicellular. Pigments: chemicals that produce color. Algae can be green, yellow, red, brown, orange or black. Algae are a major producer of Earth s oxygen, and are a major food source for aquatic organisms. http://university.uog.edu/botany/474/fw/pandorina.htm
Diatoms Diatoms: Unicellular protists with beautiful glasslike cell walls. Diatoms form a major part of the plankton in both fresh water and ocean water. They are responsible for about 20% of the Earth s photosynthesis.
Dinoflagellates Dinoflagellates (Gk dinos whirling ) are unicellular algae surrounded by tough plates. Each dinoflagellate moves like a twirling top due to its pair of flagella. They are photosynthetic autotrophs that form a major part of plankton. http://mybay.umd.edu/specifichabs.html http://withfriendship.com/user/sathvi/dinoflagellate.php
Dinoflagellates: Red Tides Some dinoflagellates have occasional population explosions called blooms or red tides. Water may be colored red, orange, or brown. Some of the red tide dinoflagellates produce a toxin that attacks the nervous system of fish, leading to massive fish kills. Humans can contract paralytic shellfish poisoning.
Euglenoids http://www.angelfire.com/ks3/merickson/Protista.html http://www.infovisual.info/02/001_en.html Euglenoids, including Euglena acus, are unicellular. Euglenoids have a stigma or eyespot that contains pigments. The eyespot is sensitive to light.
Red Algae The red algae are multicellular red seaweeds. These algae can absorb light for photosynthesis in deep ocean waters. Nori is the Japanese name for the edible red algae of the genus Porphyra. Carrageenan is a substance extracted from red algae that is added to ice cream to provide a thick, creamy texture.
Green algae Green algae: range from unicellular to multicellular green seaweeds. Contain the same pigments (chlorophyll) as land plants. Ulva sp. Sea lettuce http://3.bp.blogspot.com/-rREUo34OuOc/TaxFBtzCaAI/AAAAAAAAHDM/Z34BaFt8bwE/s400/spirogyra.jpg Spirogyra sp. http://ivan-roberto.blogspot.com/
Green algae Chlamydomonas Codium fragile Volvox sp. Udotea glaucescens
Brown algae Brown algae: contain the brown pigment fucoxanthin and also green, yellow, and orange pigments. These are the seaweeds and giant kelps (some up to 100 meters long). http://cherylyoung.files.wordpress.com/2010/08/s06.jpg?w=500h=322 http://bcadayatatime.com/2010/08/22/this-is-the-reason-we-choose-the-sea-otter-for-our-logo-hes-tops-with-us-at-bc-a-day-at-a-time/
Brown algae Substances called algins are extracted from brown algae and are used as thickeners in puddings and other foods. http://www.meijer.com/s/hunts-snack-pack-pudding-chocolate-1-multi-pack-4- cups/_/R-146289 http://www.calacademy.org/teachers/resources/lessons/sensational-seaweed/
In what section of the book store do brown algae hang out?The Self-Kelp Section www.flickr.com
Fungus-like Protists slimemoldsoralien236 The funguslike protists are heterotrophs that have cell walls and use spores to reproduce. Spore: a tiny cell that is able to grow into a new organism.
Slime Mold Life Cycle http://www.bio.miami.edu/dana/160/160S10_12.html
Slime Molds http://174.132.159.253/~jfrazer/wp-content/uploads/2010/03/flickr_plasmodium1.jpg http://theartfulamoeba.com/2010/03/25/the-math-of-natural-beauty/ Slime molds may be microscopic to large enough to cover an area of several meters. Some form many celled masses, some form a giant multinucleate cell.
Water Molds Funguslike Protists The water molds are funguslike protists that live in water and moist places. Some are important decomposers of dead aquatic organisms. Others are parasites that cause devastating crop loss (e.g. Phytophthora infestans cause of the Irish Potato Famine) File:Phytophtora infestans-effects.jpg http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Phytophtora_infestans-effects.jpg http://faculty.ccri.edu/lmfrolich/Microbiology/eukaryotes.htm
Downy Mildew Funguslike Protists File:Peronospora hyoscyami f. sp. tabacina.jpg Downy mildews are funguslike protists that are parasites of many important crops. Downy mildews grow on and infect grapes, squash, watermelons, tobacco, mint, hops and many other crops. These protists grow best in moist, humid conditions. They look like fuzz or gray-fuzzy growth on the underside of leaves (e.g. Peronospora tabacina). http://www.uvm.edu/cmb/faculty_details.php?people_id=120
Funguslike Protists Downy Mildews http://blogs.cornell.edu/ccesummerinterns/files/2011/07/100_3776.JPG http://www.apsnet.org/publications/imageresources/Pages/IW00003a.aspx Left: Downy Mildew- bottom side of leaf. Right: Light micrograph (400 ) of sporangiophore and sporangia of downy mildew (Peronospora parasitica) in tissues of shepherd s-purse plant.
Miss Kingdom Protista: Who is she? Sarcodines Amoeba proteus Algae Red algae Green algae Ciliates Paramecium bursaria Flagellates Giardia lamblia Brown algae Trichonympha campanula Funguslike protists Parasitic Protozoa Plasmodium falciparum Slime molds Toxoplasma gondii Water molds (Phytophthora infestans) Algae Diatoms Dinoflagellates Leishmania donovani Downy mildew (Peronospora tabacina) Euglenoids Euglena acus
Works Cited Brown algae. http://www.williamsclass.com/SixthScienceWork/Classification/ClassificationNotes/ClassificationNotes.htm. Chlamydomonas. https://wiki.umn.edu/IBS8102/030410-Molnar. Codium fragile. http://myweb.dal.ca/rescheib/codium.html. Diatoms. http://www.sciencephoto.com/image/15841/530wm/B3050136-LM_of_an_array_of_marine_diatoms-SPL.jpg. Diatoms black background. http://www.sciencephoto.com/media/73148/enlarge. Downy. http://momsneedtoknow.com/hot-downy-11-coupon/. Downy mildew on tobacco. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Peronospora_hyoscyami_f._sp._tabacina.jpg. Nori rolls. http://gliving.com/nori-rolls-with-pecan-pate/. Otter and kelp. http://bcadayatatime.com/2010/08/22/this-is-the-reason-we-choose-the-sea-otter-for-our-logo-hes- tops-with-us-at-bc-a-day-at-a-time. Pandorina. http://www.biosci.ohio- state.edu/~plantbio/osu_pcmb/pcmb_lab_resources/pcmb102_activities/algae_mosses/algae_mosses_pandorina.htm Red algae. http://www.barwonbluff.com.au/bluff%20life/below%20waves/marine%20plants/algae/red%20algae/pages/soft%20red%20al gae.htm. Slime mold. http://indianapublicmedia.org/amomentofscience/slime-molds-aliens/. Slime mold-pink. pinterest.com. Spirogyra species. http://www.phenomenica.com/2011/04/land-plants-evolved-from-conjugating.html. Udotea glaucescens. http://www.algaebase.org/search/species/detail/?species_id=3817&- session=abv4:42F9422A0f048236D6rRm1AB2C30. Volvox. http://www.microscopy-uk.org.uk/mag/indexmag.html?http://www.microscopy-uk.org.uk/mag/artdec03/volvox.html.