Exploring Linear Relationships in Grade 8/9 Math Curriculum
Delve into the world of linear relationships in Grade 8/9 Math curriculum, where students learn to identify, represent, analyze, and apply two-variable linear equations. Through a variety of activities and goals focused on reasoning, communication, and self-regulation, students develop a deep understanding of how discrete linear relationships can be utilized in different forms to make generalizations and solve real-world problems.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
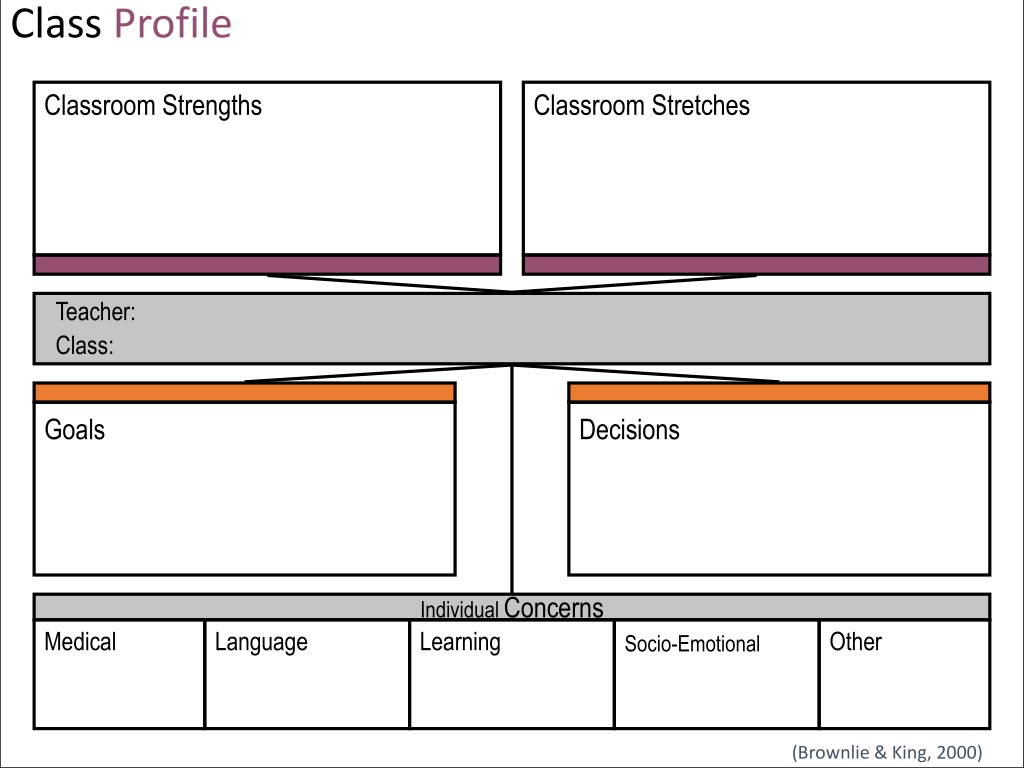
Class Profile Classroom Strengths Classroom Stretches Teacher: Class: Goals Decisions Individual Concerns Learning Medical Language Other Socio-Emotional (Brownlie & King, 2000)
RTI Triangle: Gr. 8/9 Lens: Math 9 Algebra fs Tier 3 Tier 2 Tier 1 Inclusion Planning Workshop (RTI) Shelley Moore 2017
RTI Triangle Students who need the most support Grade/Course/Subject (place) Gr. 8/9 GT (H) CH (K) LL (C/D) JH(D/C/R) CL (Q) Curricular Lens: RB (R) Tier 3 Math 9- Algebra TC (Q) MD (Q) AS (Q) GH (H) TO MD (Q) KM (K) Competency Lens: AS (Q) Social Emotional/Anxiety SH (Q) Tier 2 LL (C/D) CL (Q) SH (Q) DM (H) JP JH (D/C/R) KM (K) JB (R) CO (Q) JB (R) TC (Q) GH (H) CO (Q) BG (Q) CH (K) DM (H) JP GT (H) TO Students who need the most challenge TD ML (Q) GE GE ML BG(Q) Tier 1 Core Competency Curricular
Grade: Subject Area: Planning Team: Big Idea: Discrete linear relationships can be represented in many connected ways and used to identify and make generalizations. Unit Guiding question: What is a linear relationship? What are the different ways we can represent a linear relationship? Where could we find linear relationships in our world? Content Goal I know two-variable linear relations Curricular Competency Goal I can reason and analyse by using patterns and logic Curricular Competency Goal I can understand and solve by devloping, demonstrating, and applying mathematical understanding through play, inquiry, and problem solving Curricular Competency Goal I can communicate and represent by explaining and justifying Core Competency Goal I can self regulate in math
Course/Subject/Grade(s): Grade 8/9 Math Planning Team: Westview Secondary Unit Guiding Question: What is a linear relationship? What are the different ways we can represent a linear relationship? Where could we find linear relationships in our world? ACCESS: This is what I need to know and do ALL: This is what I must know & do MOST: This is what I can know & do FEW: This is what I could know & do CHALLENGE: This is what I can try to know & do Content Goal(s): I know 2 variable linear equations I know the difference between a letter and a number I know a real life example of an algebraic equation I know how to graph a linear equation I know how to interpolate and extrapolate approximate values I know that a linear equation can be represented in different forms I can reason and analyse by using patterns and logic I can represent a number with a variable I can use logic and reason to play puzzles and games I can make connections I can make predictions I can make inductive/deductive reasoning I can draw a conclusion I can extrapolate data into real life situations I can understand and solve by devloping, demonstrating, and applying mathematical understanding through play, inquiry, and problem solving I can participate in math activities through play I can apply mathematical strategies through play I can apply mathematical strategies through problem solving I can apply mathematical strategies through inquiry I can apply mathematical strategies to make inferences Curricular Competency Goals I can communicate and represent by explaining and justifying I can show joint attention in a mathematical activity I can communicate my thinking concretely I can represent my thinking visually I can communicate my thinking abstractly I can justify my thinking Core Competency Goal: I can become a self regulated learning I can show happy, if I like something or not I can recognize emotions I can manage my feelings and emotions I can persevere through challenging tasks I can implement, monitor, and adjust a plan and assess the results. Learning Map adapted from Cameron & Gregory, 2011 Shelley Moore, 2017
Unit Mini Lesson Planner Course/Subject/Grade(s): Unit Question: Mini lesson Planner Chunk 1 Curricular Competency question: Content Mini lesson: CC Mini lesson: CC Mini lesson: CC Mini lesson: Chunk 2 Curricular Competency question: Content Mini lesson: CC Mini lesson: CC Mini lesson: CC Mini lesson: Chunk 3 Curricular Competency question: Content Mini lesson: CC Mini lesson: CC Mini lesson: CC Mini lesson: Chunk 4 How will I demonstrate my learning? Mini lesson: e.g. What format will I choose to help me answer the guiding question? Mini lesson: e.g. What goals have I met? Mini lesson: e.g. What evidence supports my learning? Mini lesson: e.g. How can I peer/self assess? Curricular Competency Mini Lesson Planner Shelley Moore, 2017
Guiding Unit Question: What is a linear relationship? What are the different ways we can represent a linear relationship? Where could we find linear relationships in our world? Lesson Goal(s): I know a real life example of an algebraic equation Date: Connecting Activity: Put equations on the board (without letters) students write answer on the board. Slowly introduce variables and multiplication What do you notice? Essential Supports (designed for 1, useful for 1) - Safety plan - Knowing gestures/phrases - Basket of calming activities puzzles, play doh, colouring, beads Mini Lesson: 1 variable Taking the bus! Catherine is bus driver! 5 stops 3 kids at each stop as we pick up people how many now bus stop (TO, GT, LL) 3 people at each stop On the bus we will ask the bus stops how many people at your stop? make a T Chart What do you notice? What would stop 6 be? Stop 7? Processing Tasks Targeted Support (designed for some, useful for some) Choice of: - Multiplication grids - Calculators - Structured grouping I Could I Must I Can I Need to I Can Try to I can calculate a new sequence I can calculate the sequence of the bus stop I can predict the sequence of more bus stops I can count the number of people at my bus stop I can predict a new sequence Universal Supports (designed for some, useful for all) - white board - Graphic organizers - Concrete, hand on activities - Choice of work space and who to work with Few All Access Most Challenge Transforming & Personalizing Activity: What do letters represent in algebraic equations? Where is another example in the world where algebraic equations would be helpful? Lesson Planning Template Shelley Moore, 2017 Adapted from Brownlie & Schnellert