AeroFarms: Revolutionizing Vertical Farming for a Sustainable Future
Discover how AeroFarms is tackling global food challenges through innovative vertical farming techniques in dense urban spaces. Explore their strategies to address key industry challenges and create a sustainable, high-variety, and environmentally conscious business model.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
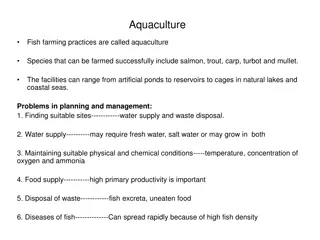
AEROFARMS A BETTER WAY TO FEED HUMANITY GSB Consulting Group
SITUATIONAL ANALYSIS Global climate and population crisis led to the birth of Vertical Farming Effective in dense urban areas, low water, land, soil, pesticide usage Can Vertical Farming solve the world s food problem? Funding becoming scarce with US legislation Growing concerns over Energy usage How will AeroFarms respond to the challenges facing the vertical farming industry to create a sustainable and profitable business model?
VALUE PROMISE AND FUTURE STATE 5 Year Strategy to ensure a sustainable and profitable business through brand repositioning, geographic expansion, talent acquisition. Revenue/ average farm 5.9m Carbon Footprint =Neutral 25 Global Farms AeroFarms, a better way to feed humanity. To combat limited crop variety, funding, high energy consumption and talent scarcity concerns.
KEY ISSUES Limited crop variety Lack of organic certification High energy consumption Brand Perception US Venture Capital regulation Access to Finance Growers hard to find Lack of training programs Complex operations with several 100 SOPs Talent Scarcity
RECOMMENDATIONS Brand Repositioning Strategy Crop variety Organic Certification Offset Carbon Footprint Geographic Expansion Strategy UK Pilot European Mid-Term Asia-Pacific Long-Term Talent Acquisition Strategy University Partnerships Develop Vertical Farming Degrees
ANALYSIS JANE
POSITIONING MAP High Variety Global vertical farming market expected to grow to US$12.77bn by 2026 Growing demand for vertical farms: Low environmental impact High environmental impact Climate change, Population growth, global food crisis & urbanisation Vertical farms generate 10x more carbon footprint than traditional Aerofarm Trends toward organic, healthy food and environmental impact Low Variety Aerofarm needs to address their environmental impact and increase variety
VALUE PROPOSITION VS CUSTOMER NEED CUSTOMER NEED Aerofarm Aerofarm: 95% less water and zero pesticides Fresh & tasty Unaffected by seasons & climate, short-lead times and close proximity Low, no protein rich offerings Minimal environmental impact High production efficiency 390x more efficient than traditional farms Product variety Environmentally friendly Lower usage of natural resources but High energy usage High production capacity & availability But, Low consumer awareness Healthy No pesticides No organic certification Comparable to organic Affordability Aerofarm needs to reposition its brand, grow customer awareness and increase variety to meet consumer needs
ACCESS TO FINANCE GEOGRAPHIC EXPANSION Hong Kong +++ London Amsterdam US$238m in funding (highest of competitors) Low profitability and high capital requirements Population density Property cost Consumer demand Food imports ++ + US Trade tensions potential for ban on international venture capitalist funding +++ ++ + Need for scale - increase farms from 9 to 25 by 2022 ++ ++ + +++ +++ ++ Aerofarm should expand internationally to grow, increase reach and improve profitability
ALTERNATIVES AND PATH FORWARD SHIVANI
RECOMMENDATIONS Brand Repositioning Strategy Crop variety Organic Certification Offset Carbon Footprint Geographic Expansion Strategy UK Pilot European Mid-Term Asia-Pacific Long-Term Talent Acquisition Strategy University Partnerships Develop Vertical Farming Degrees
ALTERNATIVES Solar- powered Vertical Farms Consumer product- Downstream Integration Farmer Finance Model
DECISION CRITERIA 1. Profitability 2. Growth 4. Brand Perception 3. Sustainability
DECISION MATRIX Profitability Growth Sustainability Brand Perception Brand Repositioning Strategy Geographic Expansion Strategy Talent Acquisition Strategy Farmer Franchising Model (alt) Solar-powered Farms (alt) Consumables (alt) High Capex, low profitability High Capex Not a core competency
DECISION MATRIX Profitability Growth Sustainability Brand Perception Brand Repositioning Strategy Geographic Expansion Strategy Talent Acquisition Strategy Farmer Franchising Model (alt) Solar-powered Farms (alt) Consumables (alt)
REC I: BRAND REPOSITIONING STRATEGY Why? Crop development into legumes, lentils and beans- nutrient/calorie dense foods Consumer, government and analyst faith in vertical farming as the solution Why? Lobby USDA for organic approval for vertical farming Consumer buy-in from organic segment who want to make the sustainable choice Why? Offset carbon emissions through tree planting projects globally Change consumer perception about Vertical- Farming not being eco-friendly Outcome: Consumer concerns and analyst skepticism around Vertical Farming will be addressed
REC II: GEOGRAPHIC EXPANSION STRATEGY Why? Expand to non-US cities- 16 additional global farms Limited access to VC funding in US, global demand in large dense urban areas Why? UK Pilot Strategy Brexit opportunity, existing VC funders Why? Mid-Term expansion through Europe and Long-Term Asia-Pacific Expansion Largest markets for Vertical Farming, existing VC funders Outcome: Global presence with unencumbered access to VC funding
REC III: TALENT ACQUISITION STRATEGY Why? Using 100+ SOPs develop university minors and technical degrees for Vertical Farming Provide job specific training at low cost to company Why? Create scholarship programs for talent pipelines at major Agricultural Universities such as Texas A&M. Create awareness about industry and harness talent early Outcome: Address talent scarcity and create skilled labour for vertical farming future
IMPLEMENTATION KATE
IMPLEMENTATION I: BRAND REPOSITIONING STRATEGY END CUSTOMER: First world Affluent High earning Environmentally conscious Move towards vegetarian and vegan Fresh and tasty New and exciting Environmen tally friendly and organic CUSTOMER VALUE
IMPLEMENTATION I: BRAND REPOSITIONING STRATEGY ORGANIC $1M to fund research into organic certification can be linked to talent strategy Collaborate with foundation of food and agri research USA help with lobbing USA VARIETY Move towards legumes and lentils Type of sprout similar growth High protein Popular to consumer in consumer profile ENERGY Launch of key initiative THE SPECBOOM INITIATIVE High carbon neutralizing plant on earth Land is cheap and proven through other initiatives Partner with ECOSIA These initiatives will solve the misalignment of consumer preferences and product offerings
IMPLEMENTATION I: BRAND REPOSITIONING STRATEGY FROM YOUR BACKYARD CAMPAIGN Consumer profile health and environmentally conscious foodies Restaurant Partner with popular chefs Develop recipes for their menus and create a customer experience Product endorsement shown in store and on social media Make sure patent appear in menus Supermarket Instore adverting in and endorsements Recipe cards displayed with products Chef endorsement
IMPLEMENTATION II: GEOGRAPHIC EXPANSION STRATEGY LONDON (3) MANCHESTER (3) LIVERPOOL (3) High population density lack of space for city farming Similar consumer profile Access to finance Brexit Slump in property market Difficulty in sourcing food AIRPORTS: Space is at a discount Logistics and trucking Proven to work well with aero planes
IMPLEMENTATION II: GEOGRAPHIC EXPANSION STRATEGY Y1 Y2 Y3 Y4 Y5 Launch from your backyard campaign Set aside $1m for organic research Research and development into legumes Sales of legumes Spec boom initiatives London Manchester Liverpool EU and Asia Pacific Review universities and develop courses Student funding
FINANCE VAN ZYL
COST BUDGET 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 Total USDA Registration Marketing Farms Development Carbon cancelling farms R&D University Partnership Total $ $ $ $ $ $ $ 1,000,000 4,350,500 30,000,000 3,593,333 2,486,000 750,000 36,829,333 $ $ 75,000,000 $ 5,226,667 $ 3,648,000 $ $ 84,624,667 $ - $ $ 45,000,000 $ 6,206,667 $ 4,370,000 $ $ 55,826,667 $ - $ $ 45,000,000 $ 7,186,667 $ 5,104,000 $ $ 57,540,667 $ - $ 10,325,000 $ 45,000,000 $ 8,166,667 $ 5,900,000 $ $ 59,316,667 $ - 1,000,000 37,639,000 240,000,000 $ 30,380,000 $ 21,508,000 $ 2,250,000 $ 332,777,000 $ $ $ 6,384,000 7,647,500 8,932,000 750,000 250,000 250,000 250,000 Raise additional funding from current funders and other environmentally focused investors.
KEY DRIVERS, UNIT ECONOMICS AND ASSUMPTIONS Current Future Note Capex Avg capex per Farm $ 19,500,000 $ 15,000,000 Lower property costs and less R&D Production Tonnes per farm 2,000,000 2,000,000 Finance Revenue per farm $ 5,600,000 $ 5,900,000 Higher value products & improved brand perception Scale of admin & marketing (FC) Costs per farm $ 5,320,000 $ 5,000,000 Ratios EBITDA Margin ROIC 5.00% 0.07% 15.25% Scale & operating leverage 6.00%
FORECASTS 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 Farms 9 11 16 19 22 25 Tonnes Produce Revenue $ 18,000,000 50,400,000 $ 22,000,000 62,150,000 $ 32,000,000 91,200,000 38,000,000 109,250,000 $ 44,000,000 127,600,000 $ 50,000,000 147,500,000 $ EBITDA $ 2,520,000 $ 4,039,750 $ 8,390,400 $ 12,345,250 $ 17,226,000 $ 22,493,750 EBITDA % 5.00% 6.50% 9.20% 11.30% 13.50% 15.25% Total Investment 332,895,833 $ Base Case ROIC Bear Case Bull Case 6.00% 3.20% 9.20% Financial ROIC + Environmental ROIC
RISKS AND CONTINGENCIES Risks Contingencies Challenges to farm new types of produce Collaboration with leading agronomists Employ British workers. Separate legal entity UK VC shareholders. Risk of Brexit impacting UK expansion Solar tech becoming cheaper. Consider to add to farms in sunny cities. Long-term continued high energy usage
CONCLUSION SHIVANI
CONCLUSION How will AeroFarms respond to the challenges facing the vertical farming industry to create a sustainable and profitable business model? Brand Perception Brand Repositioning Strategy Access to Finance Geographic Strategy Talent Scarcity Talent Acquisition Strategy AeroFarms, a better way to feed humanity. Revenue/ average farm 5.9m Carbon Footprint =Neutral 25 Global Farms
SWOT ThreatsCompetitive landscape Climate change Strengths Opportunities Weaknesses and substitutes Talent shortage VC funding and potential US ban on foreign funding Production efficiency less water, fertilization and no pestiscides 10x more capacity than traditional farms Leveraging data for customer preferences Short lead-times and less fluctuation in cost Ease of Location and proximity to customers High Capex- Lack of product diversity and low calorie, nutrient- rich food High energy usage and high carbon footprint Added vitamins & plant enhancements Customisation & other crops Previously abandoned industrial spaces Partnerships