Understanding Protein Production and the Genetic Code in Biology Class
In this biology lesson, students learn about Messenger RNA (mRNA) and its role in protein synthesis. They explore the history of DNA discovery, study leading biologists, and understand the significance of proteins in growth, repair, and other functions in organisms. The lesson also revisits the genetic code and gene expression, emphasizing the importance of proteins in creating physical differences among individuals.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
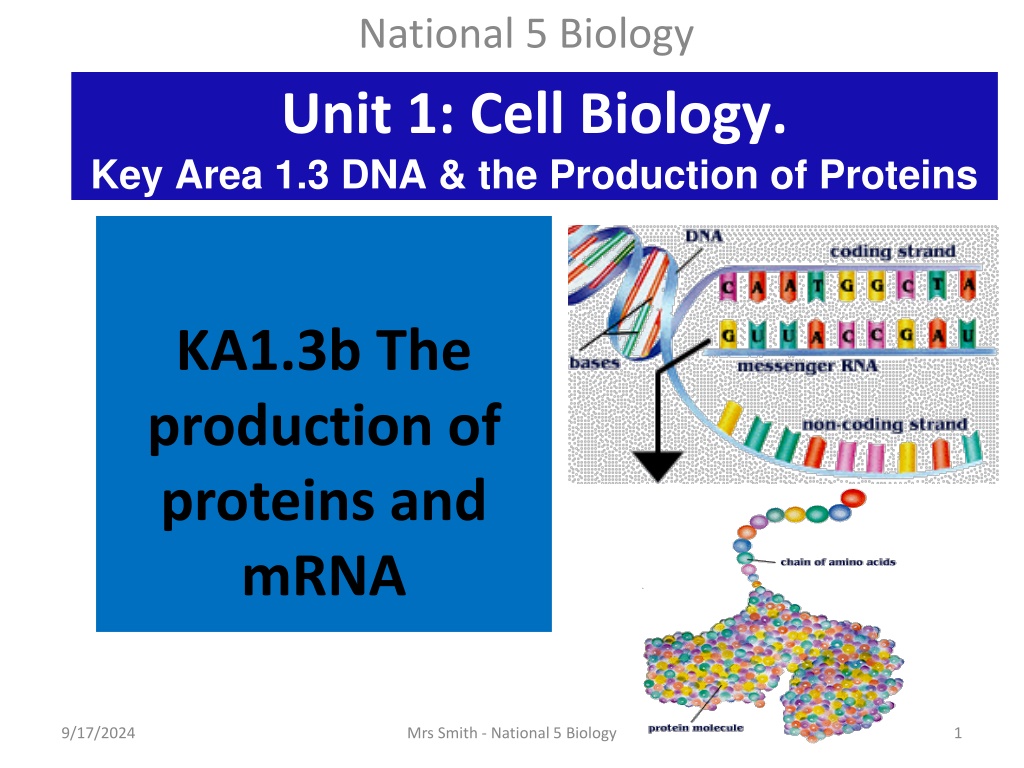
National 5 Biology Unit 1: Cell Biology. Key Area 1.3 DNA & the Production of Proteins KA1.3b The production of proteins and mRNA 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 1
National 5 Biology Learning Intentions By the end of today s lesson you should be able to: 1. Describe that Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a molecule which carries a complementary copy of the code from the DNA, in the nucleus, to a ribosome, where the protein is assembled from amino acids. 2. Have performed research on leading biologists of this area, e.g. Watson and Crick, Rosalind Franklin, Maurice Wilkins, Chargaff. 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 2
Homework: Research task History of DNA Discovery 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 3
Watch this for homework: You can also look at pg 31 Torrance http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j3jRH2fXieY 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 4
National 5 Biology Unit 1: Cell Biology. Key Area 1.3 DNA & the Production of Proteins KA1.3b Introduction to the structure and function of Protein 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 5
We are going to learn how a organism makes proteins, but what are the needed for? Growth (including making new cells) Repair of damaged tissue Building structures Muscle Bone Skin Hair Enzymes Antibodies Hormones 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 6
How the Genetic Code Works: Revision from last lesson Our bodies are made from hundreds of thousands of different kinds of _______. Small differences in the proteins that our bodies are made of account for _______ ___________ between us. protein Each gene codes for one protein. ______ code for the proteins, so small differences in our genes cause the differences between our proteins, and so the differences between us. Genes physical differences 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 7
Making proteins Proteins are long molecules made up of amino acids. protein molecule amino acid There are 20 different types of amino acid from which to make proteins. Different combinations of amino acids make different proteins. 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 8
The genetic code for the 20 amino acids (you do not need to know this!) 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 9
For Example protein molecule 1 amino acids What happens if the amino acids are in a different order? protein molecule 2 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 10
How do Genes make proteins? Each amino acid is coded for by its own special sequence of three bases called a triplet. triplet amino acid 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 11
How do genes make proteins? The order of triplets in a gene determines the sequence of amino acids. The amino acids join together to form a protein molecule. 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 12
Genes, we can investigate this in organisms by locating genes on the chromosome. By comparing 2 organisms with different traits for the same characteristic (e.g. eye colour) we can learn about the positioning and importance of genes on a chromosome. The diagram shows two identical flies with the exception of eye colour. When chromosomes are compared their genes are identical. EXCEPT for one band present in red eyed fly but absent in white eyed fly. 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 13
Once we have a chain of amino acids then the protein is folded to take on its final shape (the amino acid sequence has determined this shape). And it is this shape that allows each protein to perform its particular function. 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 14
National 5 Biology Unit 1: Cell Biology. Key Area 1.3 DNA & the Production of Proteins KA1.3b The production of proteins (protein synthesis) 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 15
The story of protein synthesis 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 16
So how does the coded information on the DNA get out into the cytoplasm? instructions Genes don t make proteins they just contain the _____________ on how to make them. BUT DNA stays in the nucleus and proteins are built in the cell s ___________. cytoplasm 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 17
Protein synthesis: The template for a protein is on the DNA, but proteins are too large to be made in the nucleus The DNA template for making proteins is held on the chromosomes, in the nucleus of a cell. Proteins are very large molecules and cannot be built in the nucleus of the cell, so must be made in the cytoplasm. (It would be like using a reference book in the library to build a car you could take all the parts into the library to make the car using the instructions in the book, but the car couldn t get out of the library. It would be too large to fit through the door!) 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 18
To solve this problem a molecule called mRNA is used. Most basic explanation. mRNA (Messenger RNA) is a messenger molecule. It is produced in the nucleus, using the DNA as a template. The mRNA then passes out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm, where it attaches to a ribosome. A new protein is assembled at the ribosome, using the mRNA and amino acids. 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 19
Basic explanation expanded on... DNA mRNA Protein DNA is kept in the nucleus to keep it safe. A specific sequence of this DNA is a gene to make a protein. This sequence is copied, so it can be taken out of the nucleus. This complimentary copy is attached to messenger RNA (mRNA). The mRNA takes the copied instructions out of the nucleus and into the cytoplasm. In the cytoplasm, the mRNA is read by a ribosome which uses the code to make the protein from amino acids. 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 20
DNA mRNA Protein Complete the diagram using the following words: Cell Nucleus Gene mRNA Ribosome Chain of amino acids DNA Membrane 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 21
DNA mRNA Protein 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 22
In sort the steps.Even more detail... can you learn this??? The information from the DNA is copied as a single strand of messenger RNA (mRNA), which takes the message from the nucleus to the ribosome, so that the protein can be built. mRNA (ribonucleic acid) is a messenger molecule made by copying the code from the DNA in the nucleus The mRNA strand leaves the nucleus through a nuclear pore and travels to a ribosome in the cytoplasm The ribosomes in the cytoplasm (or bound to the rough endoplasmic reticulum) are the site of protein synthesis in cells. At the ribosome, the code on the mRNA is read in groups of 3 bases (codon), to allow the correct amino acids to be joined together in the correct order to make the required protein. The amino acids are joined by strong chemical bonds called peptide bonds. 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 23
What happens if the code is not copies correctly?? Sometimes there are errors in the genetic code called mutations. What do you think would happen if there was an error in the genetic code for the enzyme PAH, which breaks down phenylalanine from food into useful products for the body? 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 24
Phenylketonuria: an example of only one condition due to a spelling mistake If the code is wrong, the protein is either not made or is faulty. In this case, the protein made has the wrong shape so can t carry out its job to break down phenylalanine. Instead the concentration of phenylalanine builds up in the body to toxic levels. There are many conditions which occur due to an error in the genetic code or protein synthsis 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 25
National 5 Biology Unit 1: Cell Biology. Key Area 1.3 DNA & the Production of Proteins KA1.3b Extension work for more able... with activities 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 26
Not really National 5 work but in order mRNA is a molecule different from DNA - can you suggest how? to play genetic code games you need to know this. A short section of mRNA mRNA has only one strand not two like DNA In mRNA thymine is replaced by U (uracil) U 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 27
mRNA is made using DNA template. This is called transcription. DNA inside the nucleus coding for a protein. 9/17/2024 DNA opens so that mRNA may be copied from it . Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 28
mRNA peels off the DNA template. mRNA goes out into the cytoplasm through a nuclear pore. 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 29
A real mRNA molecule would be much longer than this - the length of a whole gene. mRNA travels to a ribosome. 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 30
Out in the cytoplasm special carrier molecules pick up amino acids. mRNA moves into the ribosome so that the code it carries may be read . 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 31
Bases on the carrier molecules lock on to corresponding bases on mRNA. This brings the amino acids into line with each other and they bond together. 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 32
The carrier molecules go off into the cytoplasm to collect more amino acids. More carrier molecules continue to read the mRNA code adding amino acids and building the chain that will eventually become a protein. 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 33
TASK:To recreate the process by which a cell produces a protein. Each group of desks represents a ribosome. The teacher s desk is the nucleus. It contains the DNA sequence from which you are going to make your protein. DNA: ATCGGCATTCGCACGATCCGCAGCATT 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 34
National 5 Biology Unit 1: Cell Biology. Key Area 1.3 DNA & the Production of Proteins KA1.3b The production of proteins Extension tasks 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 35
INSTRUCTIONS Sort the bases on the mRNA molecule into codons. Use the protein decoder to work out which codon makes which amino acid. Put your amino acids together in the correct sequence. Have your protein checked by the teacher. One member of the group collect: Amino acids Sellotape White board One member of the group should nominate themselves to be mRNA. You should come to the nucleus, unzip the DNA and transcribe the sequence. 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 36
When the mRNA strand reaches the ribosome the amino acids must be joined in the order coded for by the mRNA strand. Codon on mRNA Amino acid GCG Pink UAA White UAG Blue UCG Red CCG Green UGC Yellow 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 37
Did you manage? - The Answers DNA: ATCGGCATTCGCACGATCCGCAGCATT mRNA: UAG CCG UAA GCG UGC UAG GCG UCG UAA Amino acids: blue-green-white-pink-yellow-blue-pink-red-white 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 38
Activity: Codon Bingo 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 39
Activity: DNA and Proteins Bingo ribosome guanine cytosine twenty gene sequence shape chromosome adenine base amino acid three double helix DNA protein Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology thymine messenger RNA 9/17/2024 40
Question time How many DNA bases code for each amino acid? Explain how different genes code for specific proteins. Humans have about 20,000 genes. The two members of each pair of chromosomes have the same genes on them. So, on average, about how many genes do you think there are on each of your chromosomes? When you eat proteins from meat, eggs or soya beans your body uses them to make the proteins in your cells and tissues. How do you think this happens? 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 41
A DNA Story Your Instructions: Your cast: Write a story, or draw a comic about how DNA is copied and turned into protein. The gene is a recipe for apple pie The nucleus is a library DNA is a recipe book It will feature a specific cast of characters and explain how all of the parts work together. mRNA = copy of the recipe The ribosome is a kitchen The protein made is an apple pie 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 42
Now collect the cut out and use it to tell your neighbour the story of protein synthesis. Do not cut around every base as this will be too fiddly and takes ages. Just cut up to very near the bases as shown so that you can match them up with corresponding bases. ALTERNATIVE STORY ACTIVITY 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 43
9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 44
Task TYK Complete questions 1 3. Torrance p33 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 45
Task TYK How did you do?? 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 46
Homework: DNA and protein production 9/17/2024 Mrs Smith - National 5 Biology 47