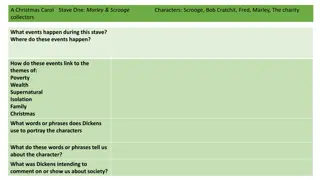
Historical Overview of 1st Maccabees: Key Events and Characters
The content provides a historical background on the book of 1st Maccabees, focusing on key dates such as the return from Babylonian captivity, construction of the Temple, and the reign of Alexander the Great. It introduces important figures like Mattathias and his sons, highlighting their role in resisting religious persecution. The narrative covers significant events such as the division of Alexander's empire and the Maccabean revolt against oppressive rulers.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
17-18 Bible Study #14 1 23 18
The Book of 1st Maccabees
Key Dates 1streturn from Babylonian captivity 538 B.C. Zerubbabel was the governor Jeshua was the high priest The Altar was built 536 B.C. (construction on the rest if temple halted for 20 years) 536 B.C. Foundation of the Temple was laid Youth rejoiced Elderly wept 534 520 B.C. work stopped due to Samaritan harassment
Key Dates (Cont) 2ndreturn 525-457 BC The prophet Haggai and Zechariah called for the people to return to the construction of the Temple Temple was dedicated 515 B.C. 3rdreturn 444 B.C. Nehemiah led the rebuilding of walls of Jerusalem 444 B.C. Ezra returned and taught in Jerusalem in 458 B.C. Persians remain in control of region
Key Dates (Cont) Alexander the Great 356-323 B.C. Defeated King Darius III of Persia in 330 B.C. Died in 323 B.C. at age 38 Succeeded by four generals who divided the empire: Ptolemy I - VI 323- 170 B.C. Controlled Egypt Defeated by a Seleucus king Seleucus I- IV - 305-175 B.C. Controlled Syria Antiochus Epiphanes defeated Ptolemy VI in 175 B.C. Controlled Palestine
Review of 1stMaccabees 1 Sets the historical background by focusing on the death Alexander the Great and the division of his empire Introduces Antiochus Epiphanes who defeats the Ptolemy dynasty in Egypt and then plundered the temple in Jerusalem King Antiochus sent a force in 141 B.C. to collect taxes, established and occupied a citadel in Jerusalem, and imposed a terrible religious persecution on the Jews
Review of 1stMaccabees 1 (Cont) Mattathias was a Levitical priest in the line of Aaron (Levite) who settled in the town of Modein This is important because he ruled even though he was not in the line of David (Judah) Yet he and his sons did many David-like things This lead some to believe that one of his sons might be the Messiah He witnessed the blasphemies being committed in Judea and he refused to offer a pagan sacrifice *
1stMaccabees (Cont) 1stMaccabees 2:1-6 Mattathias had five sons: John died Simon became the counselor Judas Maccabeus (the hammer) led the army Eleazar died Johathan founded Hazmonean Dynasty *
1stMaccabees (Cont) 1stMaccabees 2:7-15 Earlier in 1stMaccabees 1:51 we heard about King Antiochus Epiphanes appointing inspectors to go to all of the towns and villages of the country to insure that the people offered sacrifices to the Greek gods At this point one of the inspectors, with a small contingent of soldiers, arrived at Modein where Mattathias and his sons were hiding out in a somewhat faithful city *
1stMaccabees (Cont) 1stMaccabees 2:16-18 The people of the city were gathered together, the officials of Antiochus Epiphanes built a pagan altar in the city square, and announced that it was time to offer a sacrifice to their gods The officials looked to see who would keep the king s law by forsaking the Torah When they saw Mattathias and his sons (prominent members of the community), they called upon Mattathias to go first so that the rest of the community would follow *
1stMaccabees (Cont) 1stMaccabees 2:19-22 Where did Mattathias get this confidence? First, he had several grown sons and brothers who were carrying swords He and his family also controlled Modem The Greek inspector only had a few soldiers with him while all that Mattathias had to do was turn his forces on them and take control*
1stMaccabees (Cont) 1stMaccabees 2:23 Mattathias was standing there defying the king s laws and suddenly a lawbreaking Jew stepped forward to sprinkle a little incense on the altar He said that he would be happy to take some silver or gold for this act Mattathias did not take kindly to this act so he killed the Jew and then followed by killing the royal official*
1stMaccabees (Cont) 1stMaccabees 2:24-26 Remember what happened when Moses leadership was condemned by the people of Israel in the wilderness? (Numbers 25:1-14*) The Midianites sent their girls into the Hebrew camp to get the Jewish men to join in their cult prostitution as a part of their pagan worship After Moses condemned the people for their apostasy, a man (named Zimri) came to the tent of meeting with a Midianite woman Phinehas came forward with a spear and killed them both This was seen as an act of righteous anger
1stMaccabees (Cont) Mattathias committed a similar righteous act and then fled to the hills with family and followers In doing this he put his full trust in the Lord *
1stMaccabees (Cont) 1stMaccabees 2:27-41 At the outset of this rebellion, while hiding in caves, the Jews refused to fight on the Sabbath Therefore, the Greeks decided that they would always attack on the Sabbath Many Jews were killed when they refused to fight on the Sabbath
1stMaccabees (Cont) So Mattathias determined that it would not be unlawful for them to defend themselves on the Sabbath We have an allusion to this event in the Synoptic gospels when Jesus asks the Pharisees if it was all right to heal a sick person, or to do good on the Sabbath (Matthew 12:9-14) *
1stMaccabees (Cont) 1stMaccabees 2:42-50 Matthaeus was joined by a company of Hasideans The Hasideans were the holy or pious ones/mighty warriors of Israel (some see them as the forefathers of the Pharisees) Their support strengthened Mattathias movement This new group began to roam all over the country cleaning the land of the lawless men (Jews) Mattathias will begin to catechize his sons from his death bed
1stMaccabees (Cont) Here we see an example of biblical catechesis or teaching of the faith based on stories of salvation history Examples of this type of catechesis can be found in both Old and New Testament *
1stMaccabees (Con) 1stMaccabees 2:51-60 Matthaeus was reminding his sons of the stories that he had taught them since their childhood This passage can be seen as a cliff notes of all the education that he had given them since they were first able to understand his fatherly words *
1stMaccabees (Cont) 1stMaccabees 2: 61 Here he moves from the past to the present and future His sons were going to be asked to step into this story and become characters in Salvation History just as we are every time we are asked to exercise our faith *
1stMaccabees (Cont) 1stMaccabees 2:62-70 Just before his death, Mattathias reminded his sons in an abbreviated form of all that he had given them about Salvation History with emphasis on what God had done for Israel in the past He identified the roles his sons would play in this endeavor
1stMaccabees (Cont) His sons knew what God had done for Israel from the stories they had learned in their youth So their father asked them, using reason, to put their faith in God who would save them as He had saved those who preceded them in Salvation History He blessed his sons and died at Modein *
1stMaccabees (Cont) 1stMaccabees 3:1-9 Here we meet Judas Maccabees, the son of Mattathias, who: Took command of the army Defeated and killed the Greek General Apollonius Became a great and successful warrior Defeated Seron the commander of the Syrian army Prepared to fight the mighty Army of King Antiochus under the direction of Lysias at Emmaus
1stMaccabees (Cont) Again, we see the text moving back to poetry implying that it might have been sung before it returns to the historical setting Look at what Judas does with the information he was taught by his father *
1stMaccabees (Cont) 1stMaccabees 3:10-12 The Greeks, under the leadership of Apollonius, decided to gather Gentiles and Samaritans to capture and destroy Judas and his forces Instead Judas renders them a massive defeat To take the sword of your enemy was a great insult Those defeated in this battle were not only the Gentiles and Samaritans but also the lawless Jews who had forsaken the Torah and joined forces with the Greeks *
1stMaccabees (Cont) 1stMaccabees 3:13-15 Next Seron, the commander of the Syrian Army, decided to make a name for himself by defeating Maccabeus He gathered a strong organized army of ungodly men *
1stMaccabees (Cont) 1stMaccabees 3:16-26 This was like what Moses said to the people of Israel who were standing in front of the Red Sea with the most powerful army in the world coming upon them with horse and chariot (Ex 14:13-14) Judas called them to be still and wait for God to fight for them! Look at what Judas does next *
1stMaccabees (Cont) Judas had so much zeal that after his pep talk he drew his sword and rushes the enemy alone Of course his army followed Can t you hear them say there he goes again, okay lets follow him Judas was not afraid because he knew the promise God made to Israel: that one man could put to flight a thousand enemy soldiers The enemy was crushed and learned to fear the great warrior Judas Maccabaeus **
1stMaccabees (Cont) 1stMaccabees 3:27-31 King Antiochus suddenly realized that the taxes were no longer coming into his treasury This was a problem because his entire army was a paid force who did not believe in the king and had to be paid to fight for him If the pay stubs ceased his army would stop fighting On the other hand the Maccabees were fighting for their lives and the lives of their families They were also fighting for their faith in the Torah This situation led King Antiochus to divide his army and take one half into Persia to collect the tribute from the Persians in order to acquire enough money to pay for the fight against the Maccabees *
1stMaccabees (Cont) 1stMaccabees 3:32-33 Lysias was in control from the Euphrates down to the border of Egypt He was left in charge of the other half of the army when the King went to Persia He was also charged with taking care of King Antiochus son In this passage we see another reference to the use of elephants as a weapon of war *
1stMaccabees (Cont) 1stMaccabees 3:34-44 As mentioned, King Antiochus divided his army, leaving half under Lucius to finish off the rebellion in Judea while he led the rest to enforce taxation in Persia Look at the numbers Lucius brought against the Maccabees in Judea 40,000 Infantry 7,000 Cavalry Plus forces from Syria and the Philistines Up to this point the Maccabees had been primarily fighting against local Gentile forces But this was a sizable and professional army *
1stMaccabees (Cont) 1stMaccabees 3:45-47 At this point Jerusalem was under Greek control Notice that the Maccabees were not sharpening their swords, counting the size of their force, or wondering if they were strong enough to defeat such a large force Instead, they were doing the only thing that mattered they were praying and fasting as they prepared spiritually for the battle *
1stMaccabees (Cont) 1stMaccabees 3:48-53 The Gentiles were occupying the temple in Jerusalem while Judas Maccabees and his men were consulting the Torah Notice that the Maccabees did not rely upon their own military might Look at what they had already accomplished But instead of believing , based on their past victories, that they could do it again, they turned to Yahweh in prayer They knew that the odds were greatly against them, but they also knew that God was on their side *
1stMaccabees (Cont) 1stMaccabees 3:54-60 Here Judas reminded his men of the exemptions for going into battle found in the Torah to include release of: The newly married Those who recently planted a vineyard Those who were afraid (Du 20:1-9) In the end they simply put themselves in the hand of God The battle is described in the next chapter6y*