Understanding Protists: Unicellular Organisms and Their Classification
Protists are diverse unicellular organisms that can be classified based on their nutrition and movement methods. They include protozoans, algae, and heterotrophs like molds, each playing unique roles in ecosystems. From Didinium to multicellular algae, explore the fascinating world of these microscopic creatures.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
By Dr. Hesnaa Saeed Al-Mossawi
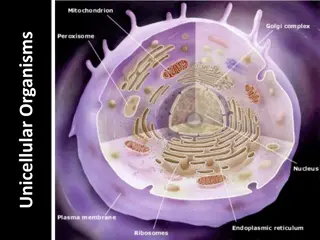
Didinium Protists are unicellular organisms that have a nucleus. Can be classified according to their nutrition: a. Animal-like heterotrophs (eat other organisms) b. Plant-like autotrophs They contain chloroplasts and make their own food (photosynthesis). a. Fungus-like Decomposers/Heterotrophs Paramecium Green like plants! Water mold
Called Protozoans Unicellular Require water (live in water or moist soil) Most heterotrophic Some photosynthetic Most are free-living Some parasitic 1. Classified according to the Method of Movement: a. Cilia hair-like projections used for movement and feeding b. Cytoplasmic streaming pseudopod (false foot) extends and cytoplasm streams into it. c. Have a Flagellum: a long whip-like structure used for movement. d. all Sporozans are parasites(no movements) ,They feed on cells and body fluids, formed from Spores (tiny reproductive cells).
Unicellular and Multicellular Colonies (groups of unicellular protists) Can move on their own Autotrophs: make their own food from simple materials using light energy (photosynthesis). Pigments: chemicals that produce color 3. Unicellular Algae: a. Phytoplankton provides a source of nourishment for other organisms b. b. Protists recycle sewage and waste materials. c. Algal blooms are harmful when overgrown deplete water of nutrients consequently killing fish. 4. Multicellular Algae: a. Red Algae b. Green Algae c. Brown Algae
Heterotrophs Have cell walls. Many have flagella and are able to move at some point in their lives. Three types: Slime Molds, Water & Downy Molds Reproduce with Spores (tiny cell that is able to grow into a new organism) Beneficial Recycles dead organic material providing nutrients for plants. Harmful Phytophthora Infestans (water mold) caused Great Potato Famine in Ireland a.
Protozoa Amoeba Entamoeba histolytica Naegleria Acanthamoeba Flagellates Giardia lamblia Trichomonas vaginalis Trypanosoma Leishmania Ciliates Balantidium coli Sporozoa Plasmodium Cryptosporidium Toxoplasma