Internal Factors Influencing Academic Achievement: Class and Self-fulfilling Prophecy
Internal factors such as self-fulfilling prophecy, class identities, pupil-teacher labeling, and streaming in schools play a significant role in shaping academic outcomes. The self-fulfilling prophecy can impact working-class children's attainment levels, as shown in studies like Rosenthal Research. However, this concept has faced criticism. Educational triage and an A-C economy further influence how pupils are categorized and supported in academic settings. Pupil subcultures also emerge in response to labeling practices, shaping group dynamics within schools.
Uploaded on Oct 08, 2024 | 0 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
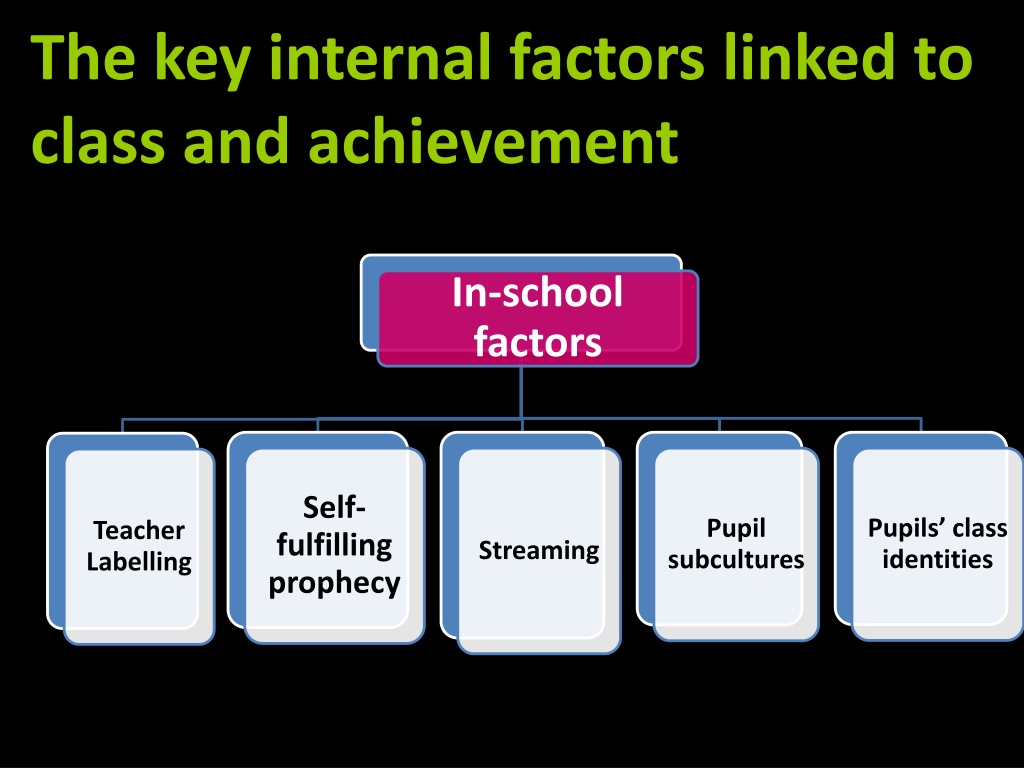
The key internal factors linked to class and achievement In-school factors Self- fulfilling prophecy Pupils class identities Pupil Teacher Labelling Streaming subcultures
PERCy Paragraph on SFP The Self fulfilling prophecy is Point It can affect a W/C childs attainment because Explain In their study, Rosenthal Research However, this idea can be criticised because Critique
Paired discussion What do these 4 terms mean? Banding Streaming Setting Mixed-ability
Streaming and self-fulfilling prophecy Streaming separate pupils according to ability and each group is taught separately. Self-fulfilling prophecy is more likely to occur when children are streamed. W/C are labelled by teachers and more likely to find themselves in lower streams locked into low expectations written off as no hopers.
Educational Triage A-C Economy Gillborn and Youdell (2001) Study of two London secondary schools. Teachers use stereotypical notions of ability to stream pupils. Less likely to see WC (and black) pupils as having ability more likely to be put into lower sets denied knowledge to gain good grades. Publishing exam league tables forces schools to focus on A-C statistics
The need to gain a good league table position creates an educational triage and A-C economy. Pupils -Triage Borderline C/D students are targeted for extra help Those who will pass anyway Hopeless cases largely ignored
Pupil Subcultures A group of pupils share similar values and behaviour patterns. Emerge as a response to labelling. Lacey (1970) Hargreaves (1967) Ball (1981) Hightown Boys Grammar School Secondary Modern Beachside Comprehensive
Lacey (1970) Hightown Boys Grammar School Participant and non- participant observation of school life. He observed and taught some lessons and helped with the cricket team. Differentiation Streaming is a form of differentiation as it categorises pupils into separate classes. Some pupils are high status others are low status. Polarisation Pupils respond to streaming by moving to extremes or opposite poles.
Pro-school subculture Anti-school subculture Pupils in low-streams (W/C) lose their self esteem. Pupils in high streams (M/C) remain committed to the school and its values. Being labelled a failure means they must gain status from other activities. Gain status from sabotaging the system which rejects him. Cheeking a teacher, Truanting, not doing homework, smoking, graffitti, vandalism.
Hargreaves (1967) Secondary Modern Boys here were triple failures. Failed the 11+, placed in low streams, labelled as worthless. These pupils seek each other out and form delinquent subculture which guaranteed their educational failure.
Ball (1981) Beachside Comprehensive Study of a school that abolishes banding in favour of mixed ability teaching. Pupil polarisation disappeared but M/C kids still did better? Differentiation between pupils continued, teachers still more likely to label M/C pupils as able. Class inequalities continued without the existence of pupil subcultures.
Other Pupil Responses to subcultures Woods (1979) Furlong (1984) pupils may drift in and out of different responses throughout their school career. Teacher s Pet Ritualism Retreatism Rebellion Not a fixed response.
Pupils class identities Archer (2010) interaction between a pupils class identity (formed outside school) and school and achievement. Habitus dispositions or learned behaviour, ways of thinking and acting shared by a class. Middle class has power to define itself as superior. The education system puts higher value on middle class culture, tastes, values.
Symbolic violence Symbolic capital Working class students seen as inferior, their preferences, clothing, accents and appearance are seen as tasteless. Middle class students are seen as worthy, having potential. WC kids see education as alien and unnatural. MC kids have symbolic capital - they share the same habitus as the education system. To be educationally successful, they felt they had to change the way they talked and presented themselves. They had to lose themselves to fit into university and professional careers.
Nike Identities WC kids seek alternative ways of creating self-worth and identity. MC see this brand fetish as tasteless young WC see it as a means of generating their own symbolic capital. Wearing brands becomes a way of being me. Nike styles signifies a lifestyle and justifies rejection of HE. Peers became style police not conforming was social suicide. WC get the message that education is not for likes of them and actively choose to reject it as it does not fit their lifestyle. Conflict with school dress code seen as rebels.
Class identity and self exclusion Evans (2009) study of 21 WC girls (A-levels) from South London. Reluctant to apply for top universities. Oxbridge not for the likes of us. We would not fit in. Self-exclusion from top universities limits options and success.
Plenary: Rank in order of importance. Justify your answer. In-school factors Self- fulfilling prophecy Pupils class identities Pupil Teacher Labelling Streaming subcultures
Home Learning 1. Define the term educational triage (2m) 2. Briefly explain how pupils identities may lead to underachievement (2m) 3. Outline three ways in which pupils may respond to streaming. (6m) 4. Evaluate the view that social class differences in achievement are the result of what goes on in schools. (20m)