Enhancing Low Latency Applications with Pre-emption in IEEE 802.11-24/103r1
Discussion on pre-emption as a solution for low latency applications in UL SU TXOP scenarios. Techniques for dividing large PPDU into smaller ones, allowing pre-emption opportunities, and enabling LL PPDU transmission after pre-emption are explored. Strategies for AP to initiate LL packet transmissions post pre-emption requests are also detailed in the document.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
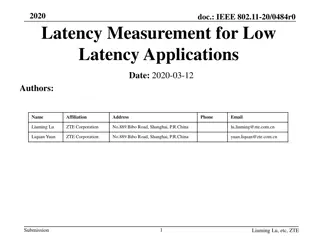
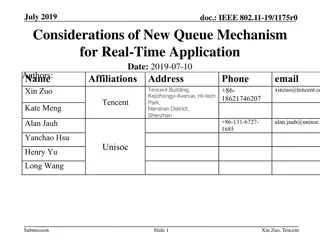
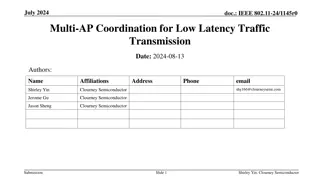
January 2024 doc.: IEEE 802.11-24/103r1 TXOP Level Pre-emption for Low Latency Application Date: 2024-01-10 Authors: Name Juan Fang Dmitry Akhmetov Minyoung Park Laurent Cariou Robert Stacey Po-kai Huang Danny Alexander Affiliations Intel Address 2111 NE 25th Ave, Hillsboro OR 97124, USA Phone email Juan.fang@intel.com Submission Slide 1 Juan Fang, Intel
January 2024 doc.: IEEE 802.11-24/103r1 Introduction Pre-emption was discussed in [1] as a general solution to support low latency application in different scenarios [2]. In this document, we will further discuss how this technique can be used in the UL SU TXOP scenario and how to send LL PPDU after pre-emption Submission Slide 2 Juan Fang, Intel
doc.: IEEE 802.11-24/103r1 January 2024 Recap - General solution for case A and case B [1] (Event-based or periodic LL traffic with jitters) Pre-emption in DL TXOP case 1. Divide the large PPDU into small PPDUs with maximum length limitation and time gaps to enable pre- emption opportunity for low latency (LL) transmitter 2. One or more LL transmitters can send common pre-emption request (PR) (similar to CTS) during the time gaps when the preemption is allowed The time gap allowed for preemption is indicated in the PPDU preceding the time gap. Shorter xIFS (??) channel access will be used for the LL transmitter (??) to send common PR. ??<?? Benefit: This avoids reserving time slot periodically within TXOP for LL traffic 3. LL packet transmission may be initiated by the AP after the reception of the common PR AP can trigger the LL STAs to send LL packet. e.g., Sending NFRP to get the LL buffer status report, then trigger the LL data transmission Slide 3 Submission Juan Fang, Intel
January 2024 doc.: IEEE 802.11-24/103r1 Pre-emption in UL SU TXOP case 1. Divide the large UL SU PPDU into small PPDUs with maximum length limitation and time gaps to enable pre-emption opportunity for the AP 2. AP can send BA with PR or other ways to indicate the pre-emption request when the pre-emption is allowed 3. LL packet transmission may be initiated by the AP after the transmission of the PR Submission Slide 4 Juan Fang, Intel
January 2024 doc.: IEEE 802.11-24/103r1 How to enable LL PPDUs after pre-emption (Event-based or periodic LL traffic with jitters) 1. PR + NFRP + NFR + TF + LL PPDU [3] 2. PR + TF + UORA for LL PPDUs 3. PR + EDCA for LL PPDUs [4] 4. PR + basic TF + BSR + TF + LL PPDUs Submission Slide 5 Juan Fang, Intel
January 2024 doc.: IEEE 802.11-24/103r1 Summary Pre-emption can provide bounded latency while keeping low performance impact to the high throughput traffic. Further consideration: xIFS time Pre-emption Request frame How to send LL packet after PR frame Further overhead reduction Submission Slide 6 Juan Fang, Intel
January 2024 doc.: IEEE 802.11-24/103r1 References [1] 11-23-0092r0, Preemption [2] 11-23-0018r1, Low latency support in UHR [3] 11-23-1229r1, Preemption-for-low-latency-application-follow-up [4] 11-23-1886r0, Preemption-techniques-to-meet-low-latency-ll-targets Submission Slide 7 Juan Fang, Intel
January 2024 doc.: IEEE 802.11-24/103r1 SP Do you agree to define a mechanism in 11bn for a TXOP holder to allow a STA associated with the TXOP holder to preempt the TXOP holder's frame exchange sequence for low latency traffic delivery NOTE: The TXOP holder can be an AP or a non-AP STA and the policy for TXOP holder allowing pre-emption is TBD Submission Slide 8 Juan Fang, Intel