Understanding Global Ecosystems and Tropical Rainforests
Ecosystems exist at various scales, influenced by both living and non-living components. Global atmospheric circulation shapes the distribution of biomes like tropical rainforests and hot deserts. Tropical rainforests, with distinct environmental characteristics, face threats like deforestation. Sustainable management is crucial. These rainforests thrive in hot climates with high precipitation, showcasing rich biodiversity and complex ecological relationships. Adapting to rapid nutrient cycling and poor soils, they harbor unique plant and animal species in different layers, emphasizing the importance of conservation efforts.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The living world Ecosystems Tropical rainforests Hot deserts We don t study cold environments.
Ecosystems Ecosystems exist at a range of scales and involve the interaction between living and non-living components. Global atmospheric circulation is the main factor in determining the distribution of large-scale global ecosystems (biomes).
Ecosystems exist at a range of scales and involve the interaction between living and non-living components. What is an ecosystem? Freshwater pond ecosystems Producers Consumers Decomposers Food chain Food web Nutrient cycling
Ecosystems exist at a range of scales and involve the interaction between living and non-living components. How changes affect ecosystems global or local scale. Natural changes drought in a pond. Human changes eutrophication, abstraction, invasive species.
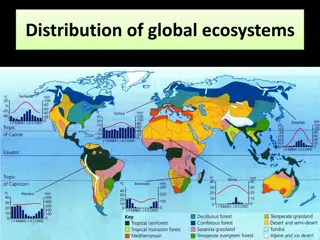
Global ecosystems Largely known by vegetation type Determined by global circulation system (north-south). East- west variations caused by ocean currents, winds, altitude, distribution of land and sea. 3 forests need significant rain TRF, deciduous and coniferous. 3 grasslands need some rain savannah, temperate (steppe or prairie), tundra. 3 deserts hot, temperate and cold (polar). Plus Mediterranean hot desert like summers, but mild, wet winters so adapted trees will grow (olive, cypress).
Tropical rainforests Tropical rainforests have distinctive environmental characteristics. Deforestation and economic and environmental impacts. Tropical rainforests need to be managed to be sustainable.
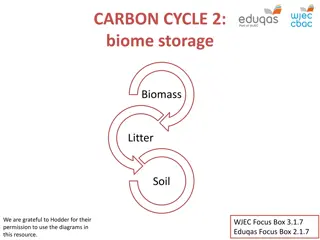
Tropical rainforests have distinctive environmental characteristics. Location in the tropics. Climate hot all year (28 degrees C). Wet 2500mm of precipitation. Most have a drier season when the equatorial low pressure area is not directly overhead. Soils poor in nutrients, red coloured, latosols. Rapid nutrient cycling (by fungi). Leaching from heavy rain. Plants and animals. Biodiverse niches in structure and huge amount of energy and water. 4 layers (emergent, canopy, under canopy, shrub layer). Most energy at canopy layer. Plant adaptations drip tips, buttress roots, epiphytes. Animal adaptations climbing, flying. Relationships are close but fragile deforestation has a huge impact.
Deforestation and economic and environmental impacts. Malaysia case study 67% forested. Deforestation caused by Logging by clear felling valuable trees mahogany, teak, rosewood. Mineral extraction tin on peninsular, oil and gas on Borneo. Dam building Bakun Dam on Borneo HEP for industry. Commercial farming palm oil (world s largest producer). Road building linked to other causes. Need roads to access raw materials. This attracts more development. Population pressure easing pressure on growing cities (transmigration policy). Subsistence farming slash and burn can get out of control.
Deforestation and economic and environmental impacts. Impacts of defrestation in Malaysia. Soil erosion Loss of biodiversity orang-utans, Main Range in Peninsular Malaysia. Contribution to climate change absorb CO2, transpiration. Economic development Employment (both direct and indirect). Improved infrastructure. Power from HEP. Valuable minerals. Economic losses Pollution, fires, loss of medicinal plants, impact of climate change, loss of tourism.
Tropical rainforests need to be managed to be sustainable. What are current rates of deforestation slowing but still happening. Over half the trf on the planet has been lost. Why protect rainforests? Biodiversity Climate change and climate People (Achuar in Peru) Medicines Resources, especially water.
Tropical rainforests need to be managed to be sustainable. Methods of sustainable management. Selective logging and replanting elephants. Conservation and education. Ecotourism (Lapa Rios in Costa Rica). Small scale, carbon neutral. International agreements. FSC Debt reduction.
Hot deserts Hot deserts have distinctive environmental characteristics. Development of hot deserts creates opportunities and challenges. Areas on the fringe of hot deserts are at risk of desertification.
Hot deserts have distinctive environmental characteristics. Location 30 degrees north and south. Usually in interiors of continents although cold currents can lead to coastal deserts. Climate dry (less than 250mm of rain) and hot during the day. Can be chilly at night. Soils sandy and lacking in organic matter. Can be salty due to rapid evaporation. Plant adaptations deep or wide roots, succulents, spikes, dormant seeds. Animal adaptations Colour, nocturnal, big ears, wide feet, burrowing, low volume urine.
Development of hot deserts creates opportunities and challenges. Thar Desert case study. Opportunities. Mineral extraction kaolin, gypsum, marble near Jodphur. Tourism safaris, winter festival, Jaisalmer is the centre. Energy solar (Bhaleri), wind (Jaisalmer Wind Park). Farming commercial farming (Indira Ghandi Canal) mustard, sesame. Subsistence farming tends to be grazing. Challenges Extreme temperature livestock and people suffer. Water supply intermittent stream and ponds, poor quality aquifer. Accessibility roads melt, rails bend, both get covered by sand storms. Camels can t carry a lot.
Areas on the fringe of hot deserts are at risk of desertification. What is desertification? Where is it a problem? Edges of deserts e.g. Sahel, including northern Nigeria. Causes overpopulation overgrazing/ overcultivation soil erosion. Also climate change. Solutions Water and soil management irrigation (avoid salinisation). National Parks Planting vegetation trees (prosopsis cineraria), shrubs (atriplex). Appropriate technology magic stones.