Understanding Ecological Succession and Its Impacts
Ecological succession is the orderly process of change in an ecosystem, where one community replaces another until a stable climax is reached. This progression affects populations and species diversity. The process involves primary and secondary succession, with events like tornadoes, hurricanes, and forest fires impacting the plant population. The ideal end of succession is the climax community. Explore the differences in pictures and learn about pioneer species that initiate succession.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
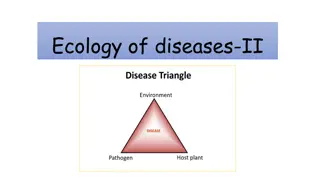
ECOLOGICAL SUCCESSION Obj: 11D Describe how events and processes that occur during ecological succession can change populations and species diversity.
What is ecological succession? orderly process of change in an ecosystem brought about by the progressive replacement of one community by another until a stable climax is established
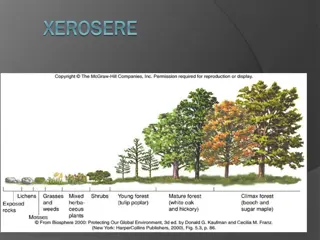
What differences do you see in these pictures?
What disasters could affect the plant population? Tornados Hurricanes Forest fires Volcanoes Floods
Climax Community The ideal end community in any given ecosystem https://ww w.youtube. com/watch ?v=iZA5yfr zLV8&feat ure=player _embedde d
Primary Succession Occurs on bare rock or hardened lava on which no soil organisms exist Beings with arrival of lichens, a pioneer species
Pioneer Species Able to grow on barren rock First organisms to grow during primary succession Ex: lichens, mosses
Secondary Succession Occurs after an event in which the ecosystem is damaged, but not destroyed. Because soil remains, secondary succession is faster than primary succession
https://www.youtube.com/watch?feature=pla yer_embedded&v=4RsMyVavT2Q
large deep lakes shallow ponds grassland
How does succession affect population size? Forest fire or volcanic eruption will decrease population and diversity If the soil is intact, over time, the populations will recover Ex: insects deposit eggs in the soil & these eggs can survive and hatch after a fire
How does succession affect population diversity? Animals that survived may move to other regions which reduced competition for other species Can lead to entirely new ecosystems if new herbivores move in where there were once none. Eventually carnivores will move in to eat new herbivores.
How do population and species diversity change as succession progresses? Population size and species diversity both increase during ecological succession Over time, more species are able to survive and become established
Smaller producers are replaced by larger ones, such as small trees and shrubs As insects increase, birds and other animals that eat insects arrive Eventually a climax community will build again