Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder: Overview and Assessment
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a lifelong neurodevelopmental condition that affects social interaction, communication, and behavior. The spectrum includes a range of characteristics, from highly verbal individuals to non-verbal ones. Various disorders fall under the ASD umbrella, with different levels of severity and manifestations. The Indian Scale for Assessment of Autism (ISAA) is used for evaluation, with scores indicating the severity of symptoms. Early diagnosis and assessment play a crucial role in understanding and managing ASD.
- Autism Spectrum Disorder
- ISAA Evaluation
- Neurodevelopmental Condition
- Social Interaction
- Communication.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
http://www.wilmingtonnc.gov/portals/0/documents/Common%20Files/images/icons/Facebook.pnghttp://www.wilmingtonnc.gov/portals/0/documents/Common%20Files/images/icons/Facebook.png Twitter https://encrypted-tbn2.google.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcQRqbNhghIhe9IAoQou1JbiCNNzzQ9vaQJynvaU1JuxAP6o9Wz_XQ http://www.wilmingtonnc.gov/portals/0/documents/Common%20Files/images/icons/Facebook.png Twitter https://encrypted-tbn2.google.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcQRqbNhghIhe9IAoQou1JbiCNNzzQ9vaQJynvaU1JuxAP6o9Wz_XQ Disability Certification in Psychiatry BY DR. PRADEEP SHARMA HOD & SUPERINTENDENT PSYCHIATRIC CENTRE, SMS, JAIPUR
What Is Autism? Lifelong Neurodevelopmental condition. Affects, among other things, the way an individual relates to his or her environment and their interaction with other people. Spectrum' describes the range of difficulties that people on the autism spectrum may experience and the degree to which they may be affected. Particular difficulties in some or all of the following areas: Communication Social interaction Imagination ( Presence of restricted interests and activities) TRIAD OF IMPAIRMENTS
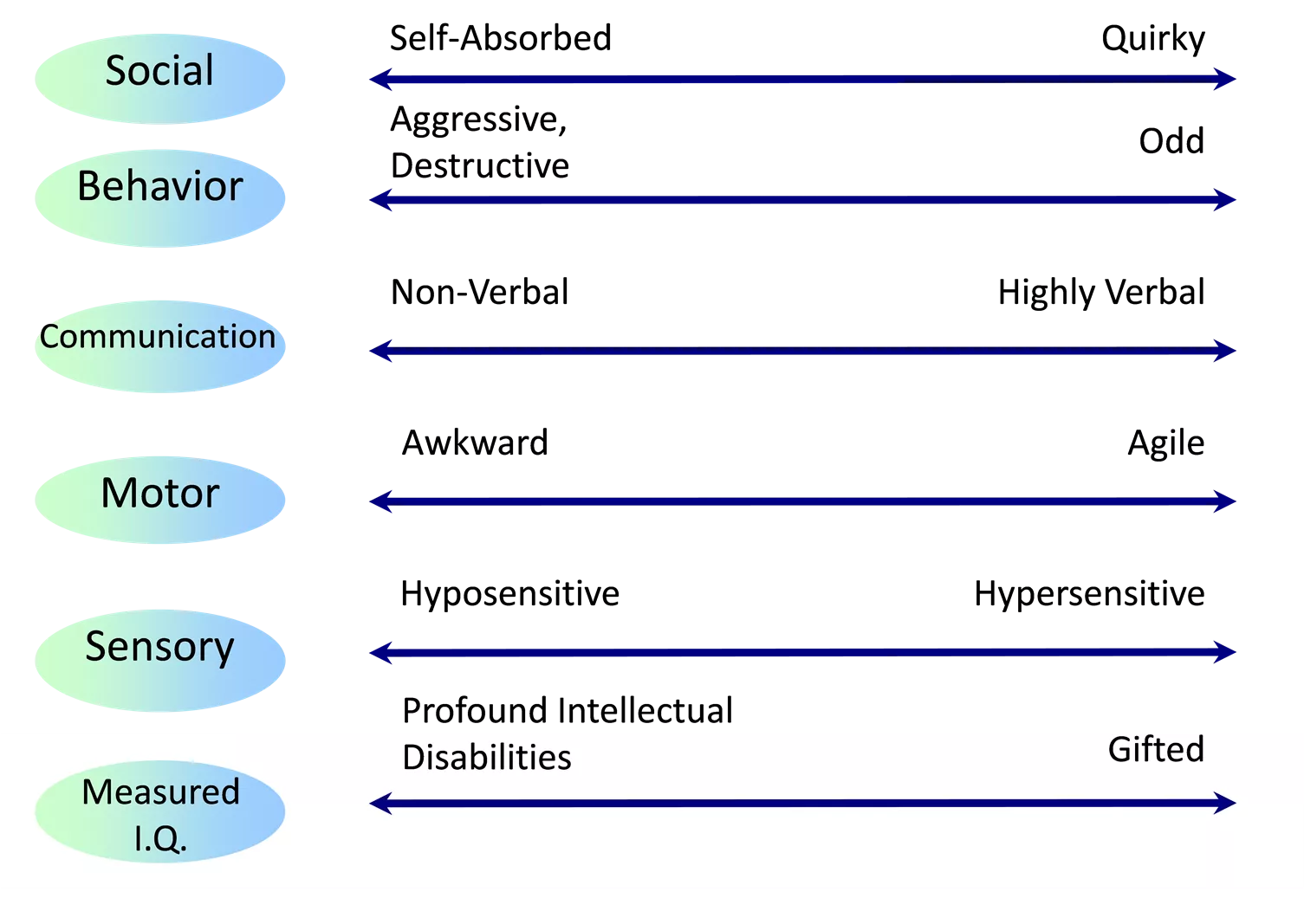
Spectrum of Autism Self-Absorbed Quirky Social Aggressive, Destructive Odd Behavior Non-Verbal Highly Verbal Communication Awkward Agile Motor Hyposensitive Hypersensitive Sensory Profound Intellectual Disabilities Gifted Measured I.Q. 3
Pervasive Developmental Disorders DSM-IV (1994-2000) DSM-IV-TR (2000-2013) . DSM-5 (2013-now) ICD-10 (1996-now) 299.00 Autistic Disorder F84.0 Childhood Autism 299.80 Asperger s Disorder F84.5 Asperger Syndrome F84.1 Atypical Autism F84.8 Other pervasive developmental disorders F84.9 Pervasive developmental disorders, unspecified F84.4 Overactive disorder associated with mental retardation and stereotyped movements F84.2 Rett s Syndrome 299.00 Autism Spectrum Disorder 299.80 Pervasive Developmental Disorder - not otherwise specified (including Atypical Autism) PDD-NOS 299.80 Rett s Disorder 299.10 Childhood Disintegrative Disorder F84.3 Childhood Disintegrative Disorder
EVALUATION AND ASSESSMENT FOR AUTISM The National Institute for Mentally Handicapped (NIMH) developed the Indian Scale for Assessment of Autism (ISAA) for diagnosing and measuring the severity of autism in 2009. It has 40 items divided under six domains social relationship and reciprocity; emotional responsiveness; speech, language and communication; behavior patterns; sensory aspects and cognitive component. The items are rated from 1 to 5, increasing score indicating increasing severity of the problem.
A score of <70 indicates no autism, 70-106 (mild autism), 107-153 (moderate autism), and >153 (severe autism). It takes about 15 to 20 minutes for administration of ISAA. The ISAA was devised with the aim of quantifying the severity of autistic symptoms so as to enable measurement of associated disability. Quantification of disability would help in getting disability benefits.
A symptom severity score of 70 in ISAA corresponds to 40% disability; 71-88 (50%), 89-105 (60%), 106-123 (70%), 124-140 (80%), 141-158 (90%), whereas >158 (100%) disability. The subgroup of mild autism (70-106) has two different disability scores and the group with moderate autism (107-153) has different disability scores. A score of 153 would mean severe autism, but 100% disability benefits can be expected only if disability score is >158.
Disability Certification in Psychiatric Practice Rehabilitation Committee of the Indian Psychiatric Society (IPS) came up with the Indian disability evaluation and assessment scale (IDEAS) in 2002. IDEAS was field tested in nine centers all over India and has now been gazetted by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, Government of India, as the recommended instrument to measure psychiatric disability. Patients with the following diagnoses are eligible for disability benefits: 1. Schizophrenia. 2. Bipolar Disorder. 3. Dementia. 4. Obsessive Compulsive Disorder. Duration of illness - = at least 2 years the number of months the patient was symptomatic in the last 2 years (M12Y months of illness) should be determined.
The IDEAS, evaluates disability in four areas (termed items in the scale), namely, Self care, Interpersonal activities, Communication and Understanding, and Work. Each item is scored on a 5 point scale with a range of 0-4, i.e. from no (0) to profound disability (4). The total disability score is obtained by summing up the ratings on each item. Global Disability Total Disability score +MI2Y score = Global Disability score (range: 1-20)
Percentages For the purpose of welfare benefits, 40% will be the cut- off point. The scores above 40% have been categorized as Moderate, Severe and Profound based on the Global disability score. This grading will be used to measure change over time. Score of 0 - No Disability = 0% 1 -7 - Mild Disability = < 40 % 8 and above = > 40 % (8 -13 Moderate Disability; 14-19 = Severe Disability; 20 = Profound Disability)
MENTAL RETARDATION A condition of arrested or incomplete development of the mind, which is especially characterised by impairment of skills manifested during the development period which contribute to the overall level of intelligence, i.e., cognitive, language, motor and social abilities. Categories of Mental Retardation Mild Mental Retardation - The range of 50 to 69 (standardised IQ test) is indicative of mild retardation. Moderate Mental Retardation - The IQ is in the range of 35 to 49. Severe Mental Retardation - The IQ is usually in the range of 20 to 34. Profound Mental Retardation - The IQ in this category estimated to be under 20.
Disability Assessment of Mental Retardation Assess the intelligent quotient (IQ). IQ to be assessed by using a standardized test like Binet Kamat Test, Alexander s Pass Along Test, Koh s Block Design test, Draw A Man Test, Sequin form board for children with MR aged above 5 years, Wechsler's Intelligence Scale. Calculate disability as follows: 110-IQ = Disability scoring. Example : If IQ is 40 the disability is 70% (110-40-70)